Electrically Actuated Canopy Seal
An electrically actuated canopy pressure seal
system is shown in figure 2-11. This type of system
is controlled by a pressure regulator and dump
valve assembly, which consists of a pressure
regulator, a solenoid poppet shutoff and vent
valve, and a relief valve.
Electrically Actuated Canopy
Pressure Seal Regulator Valve
The canopy pressure seal regulator valve
controls the pressurizing and depressurizing of the
canopy seal, depending upon the canopy position.
The pressure regulator consists of a spring-loaded
diaphragm, which controls a poppet valve to
admit the correct air pressure to the canopy seal.
An adjustment screw is provided at the top of the
regulator housing to adjust the output of air
pressure.
The shutoff and dump valve consists of a
solenoid-operated poppet valve, which is spring-
loaded to the closed position. When the solenoid
is energized (fig. 2-11, view A), the dump valve
closes the vent port and opens the regulator
shutoff to permit inflation of the canopy seal. The
outlet pressure is maintained at approximately 20
psi by the pressure regulator.
When the solenoid is de-energized by the
opening of the canopy (fig. 2-11, view B), the
dump valve opens the vent port, closes the
regulator shutoff to stop the flow of supply air,
and dumps the pressure in the canopy seal over-
board through the vent line. The relief valve
feature of the pressure regulator prevents seal
pressure from becoming excessive during rapid
altitude changes by venting the seal pressure over-
board when the pressure reaches a maximum of
22 psi (fig. 2-11, view C).
In case of an electrical failure, the reg-
ulator valve is spring-loaded in the dump
position.
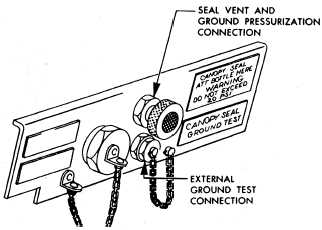
Ground Test Connections
Most canopy pressure seal systems have
ground test connections that are used to
ground test the system and to pressurize
the system during carrier deck storage. The
Figure 2-12.—Cabin air pressure test panel.
ground test connections (fig. 2-12) are usually
located on the cabin air pressure test panel.
One connection is used for ground test, and
the other, which is normally the seal vent,
is used for ground pressurization of the canopy
seal.
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance of the canopy system consists of
servicing, troubleshooting, and removal and
installation of components. The applicable air-
craft maintenance instructions manual (MIM)
furnishes such information as proper procedure,
manpower requirements, materials lists, tool and
equipment lists, quality assurance instructions,
and maintenance-level instructions for the disposi-
tion of defective parts.
Servicing
Servicing is limited to cleaning the canopy seal,
ground inflating the canopy seal, and periodic
inspections for visible defects, dirt, and foreign
material accumulations. All major components
of the system are self-sustaining and require no
general servicing between overhaul periods for
normal operation.
When pressurized aircraft are stowed on
the carrier flight deck without canopy covers,
the canopy seal should be inflated externally
to protect the cabin area. Ground pressurization
of the canopy seal is accomplished by attaching
an external air source to the canopy seal
vent and ground pressurization connection
2-15