Figure 3-5.—Passive honing system.
receives the signals reflected off the target, computes the
information, and sends electronic commands to the
control section. The control section functions in the
same manner as previously discussed.
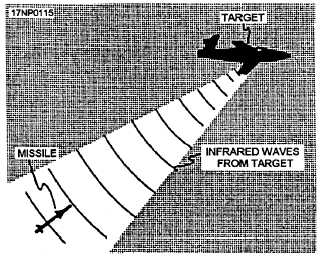
PASSIVE.— In the passive homing system (fig.
3-5), the directing intelligence is received from the
target. Examples of passive homing include homing on
a source of infrared rays (such as the hot exhaust of jet
aircraft) or radar signals (such as those transmitted by
ground radar installations). Like active homing, passive
homing is completely independent of the launching
aircraft. The missile receiver receives signals generated
by the target, and then the missile control section
functions in the same manner as previously discussed.
A1.
Armament Section
The armament system contains the payload
(explosives), fuzing, safety and arming (S&A) devices,
and target-detecting devices (TDDs).
PAYLOAD.— The payload is the element or part of
the missile that does what a particular missile is
launched to do. The payload is usually considered the
explosive charge, and is carried in the warhead of the
missile. High-explosive warheads used in air-to-air
guided missiles contain a rather small explosive charge,
generally 10 to 18 pounds of H-6, HBX, or PBX high
explosives. The payload contained in high-explosive
warheads used in air-to-surface guided missiles varies
widely, even within specific missile types, depending on
the specific mission. Large payloads, ranging up to 450
pounds, are common. Comp B and H-6 are typical
explosives used in a payload.
Most exercise warheads used with guided missiles
are pyrotechnic signaling devices. They signal fuze func-
tioning by a brilliant flash, by smoke, or both. Exercise
warheads frequently contain high explosives, which vary
from live fuzes and boosters to self-destruct charges that
can contain as much as 5 pounds of high explosive.
FUZING.— The fuzing and firing system is
normally located in or next to the missile’s warhead
section. It includes those devices and arrangements that
cause the missile’s payload to function in proper relation
to the target. The system consists of a fuze, a safety and
REVIEW NUMBER 1 ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS Q1. THROUGH Q8.
If a guided missile is traveling at Mach 1, it is traveling at approximately 766
miles per hour.
A2.
A3.
A4.
A missile traveling at Mach 3 is traveling at supersonic speeds.
The two types of guided missiles are service and nonservice guided missiles.
The two types of guided missiles used in naval aviation are air-to-air and
air-to-surface guided missiles.
A5.
A6.
A7.
A8.
Th first letter of a missile designation describes the missile's launch environment.
The missile designation ATM stands for an air-launched training guided missile.
The serial number in an assembled missile is usually found on the leading
component.
The color codes on guided missiles identify the explosive hazard in the missile
component.
3-6