MK 25 MODS 2 AND 3 MARINE LOCATION
MARKER
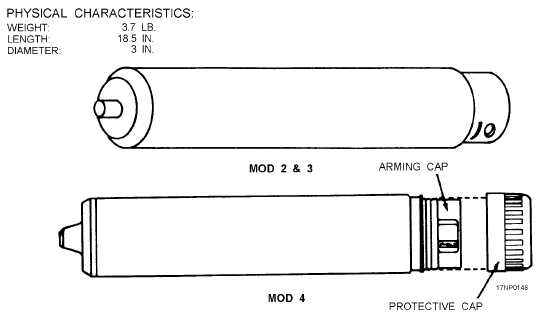
The Mk 25 Mods 2 and 3 (fig. 4-7) marine location
markers are launched from aircraft or surface craft.
They are launched from aircraft to provide day or night
reference points for marking the course of enemy
submarines in antisubmarine warfare operations. They
are suitable for any type of sea-surface reference-point
marking that calls for both smoke and flame for a
period of 10 to 20 minutes. Mods 2 and 3 function
identically. The only significant difference is that Mod
2 contains two seawater-activated batteries and two
related squibs while Mod 3 contains a single battery
and squib.
Physical Description
The Mk 25 marker consists of a cylindrical outer
tube about 18.5 inches long and 2.9 inches in diameter.
A valve assembly is fitted into the projecting chimney
at the marker's nose end. The smoke and flame are
emitted from this opening. At the opposite end is a
heavier aluminum base assembly to which the outer
tube is crimped. The heavy base end causes the marker
to float in the water with the chimney out of the water
and the base in the water.
Within the base assembly is a Mk 72 Mod 0
seawater-activated battery (two batteries in the Mod 2).
The battery is shielded from water contact by two plugs
fitted into 1/2-inch holes on two opposite sides of the
base assembly. A rigid cover (arming plate), held in
place by a retainer ring, is recessed into the base end.
An arrow in the center of the arming plate indicates its
safe or armed position. The words SAFE and ARMED
are stamped into the base rim. Also, a machined notch
in the rim at the armed position helps during night use.
When the arming plate is in the safe position, it
physically blocks the base plugs internally to prevent
them from being accidentally pushed in. When in the
armed position, the arming plate no longer blocks the
base plugs, allowing them to be pushed in at the
appropriate time. A black rubber G-ring circles the base
assembly approximately 1/4 inch from the crimp,
which holds the outer case.
Functional Description
To activate the seawater battery, the base plugs are
pushed in before the marker is actually launched. An
electric
squib
ignites
the
marker,
and
the
seawater-activated battery (two batteries and two
squibs in Mod 2) supplies power. When the marker
enters the water, seawater enters the battery cavity and
serves as an electrolyte, causing the battery to produce a
current that activates the squib. The squib ignites the
starter mix, which, in turn, ignites the red phosphorous
pyrotechnic composition. Gas buildup forces the valve
assembly from the chimney in the nose, and yellow
flame and white smoke are emitted. Burning time
averages 13.5 to 18.5 minutes. Although this marker is
normally used in seawater, it can be used in inland
bodies of fresh water by using table salt and following
the procedures outlined in Pyrotechnic, Screening,
Marking, and Countermeasure Devices, NAVSEA
SW050-AB-MMA-010/NAVAIR 11-15-7.
4-8
Figure 4-7.—Mk 25 marine location marker.