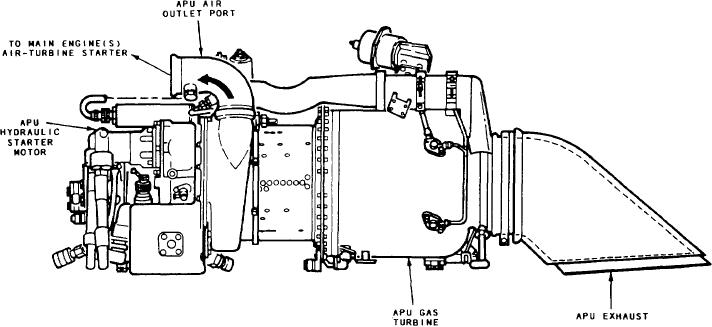
Figure 6-18.-Typical onboard auxiliary power unit (APU).
APUs are small, self-contained jet engines that
units to carry out its mission. There are many
types and configurations of gas-turbine units.
are started either electrically through onboard
Maintenance performed on APUs can be
batteries or hydraulically through a hydraulic
almost as extensive as that performed on aircraft
starter motor. See figure 6-18.
In the past, APUs were too large and too
engines. The major difference, other than the size,
heavy for practical use in tactical combat aircraft.
is that most APUs use centrifugal flow jet engines
Their use was limited to the larger land-based air-
instead of axial flow. The nomenclature of many
of the components may be the same. However,
craft with missions such as patrol, cargo,
transport, or special projects. Advancements
the component itself may not look or operate in
in technological design and metallurgy have
the same manner because of the basic function
produced small, lightweight, yet efficient APUs.
of the unit.
Authorized repairs for organizational activities
These advancements have enabled newer carrier-
include minor component replacements and
borne aircraft, such as the S-3 and the tactical
adjustments. Common repairs include inlet/
F/A-l 8, to operate aboard ship without the
requirement for flight deck support equipment.
exhaust door actuator maintenance, bleed-air
This places less demand on the flight deck crews,
shutoff valve maintenance, and generator replace-
ment. Maintenance on the ignition system,
and makes the flight deck a somewhat safer
generator, oil tank, oil pressure switch, oil cooler,
working environment.
and scavenge oil filter, or major inspections may
The use of an APU makes the modern jet air-
require APU removal because of the APU
craft completely self-sufficient. Aircraft having
location. Major APU inspections and repairs
air turbine starters can use compressed air from
are performed by the supporting intermediate
the APU to start engines. They also supply
maintenance activity (IMA) under the Auxiliary
electrical and hydraulic power, as well as air
Power Unit and Support Equipment Gas Turbine
conditioning during ground maintenance. The air-
Engine Management Program.
craft is independent of the need of ground power
6-21

