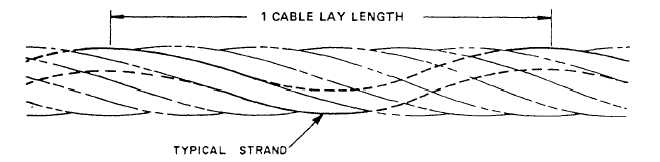
Figure 3-25.—Cable lay length.
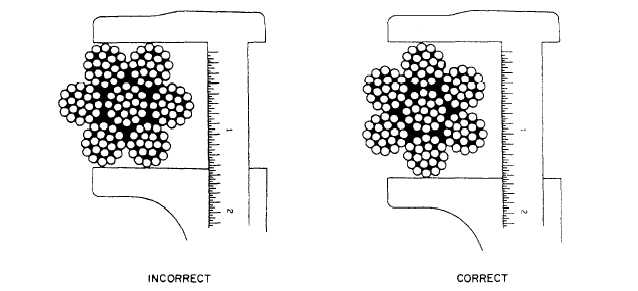
cross section. Figure 3-24 shows the proper method of
measuring the diameter of a wire rope.
2. Lay Length. The distance, parallel to the axis of
the cable, in which a strand makes one complete turn
about that axis is known as the lay length or pitch length.
Figure 3-25 shows the lay length of a wire rope.
Wire rope cables are visually inspected for knots,
fraying, stretching, abrasions, severe corrosion, and
other signs of failure. Of particular importance is the
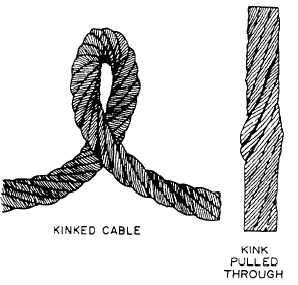
detection of a cable in which a kink has been pulled
through in order to straighten the cable. The resultant
deformation is known as a bird cage. See figure 3-26. In
such a case, the sling should be discarded.
The presence of one or more broken wires in one
rope lay length or one or more broken wires near an
attached fitting is cause for replacement. If a broken wire
is the result of corrosion or if the cable is excessively
Figure 3-26.—Cable damage resulting from a pulled-through
corroded, the cable must not be used regardless of the
kink.
3-36
Figure 3-24.—Measuring the diameter of a wire rope.