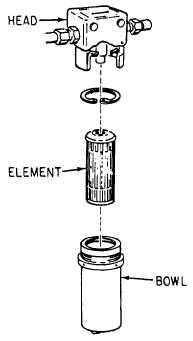
Figure 7-32.—Hydraulic filter assembly.
HEAD ASSEMBLY.—The head assembly is
secured to the aircraft structure and connecting lines.
The head assembly of some filters have a pressure-
operated bypass valve, which will route the hydraulic
fluid directly from the inlet to the outlet port if the
filter element becomes loaded with foreign matter.
BOWL—The bowl is the housing that holds the
element to the filter head, and it is removed when
element replacement is required.
FILTER ELEMENT.—The filter element may
be of the 5-micron noncleanable, woven mesh,
micronic, porous metal, or magnetic type. The
micronic and 5-micron noncleanable elements have
nonmetallic filter media, and are discarded when
removed. Porous metal, woven mesh, and magnetic
filter elements are usually designed to be cleaned and
reused.
However, some metallic filters are
considered noncleanable and are normally discarded.
Noncleanable filter elements rated at 5-microns
(absolute) represent the current state of the art in
hydraulic filtration.
Elements of this type afford
significantly improved filtration and have greater
dirt-holding capacities than other types of elements of
the same physical size. They are particularly
effective in controlling particles in the 1- to
10-micron size range, which are normally passed by
other types of elements, and they are capable of
maintaining a hydraulic system at much cleaner levels
than could previously be achieved. The use of
5-micron (absolute) filters is presently specified for
all new design aircraft, and they are being retrofitted
to existing fleet aircraft where practicable.
The most common 5-micron filter medium is
composed of organic and inorganic fibers integrally
bonded by epoxy resin and faced with a metallic mesh
upstream and downstream for protection and added
mechanical strength. Filters of this type are not to be
cleaned under any circumstances, and will be marked
DISPOSABLE or NONCLEANABLE, usually on the
bottom end cap.
Five-micron, noncleanable, hydraulic filter
elements should be replaced with new elements
during specified maintenance inspection intervals in
accordance with the applicable procedures. Refer to
the applicable MIM or maintenance requirement
cards (MRC) for replacement intervals and
procedures.
Another 5-micron filter medium of recent design
employs layers of very fine stainless steel fibers
drawn into a random but controlled matrix. The
matrix is then processed by an exclusive procedure,
which in successive steps compresses and sinters
(bonds all wires at their crossing points) the material
into a thin layer with controlled filtration charac-
teristics.
Filter elements of this material may be
cleanable or noncleanable, depending upon their
construction, and are marked accordingly.
Support Equipment (SE) Filters
To ensure delivery of contaminant-free hydraulic
fluid, all SE must be provided with 3-micron
(absolute) non-bypass filtration in their fluid
discharge or output pressure lines. With many test
stands, the filter used for this application, in addition
to having a low micron rating, must be capable of
withstanding high-collapse pressures and holding
large amounts of dirt.
Unlike most filter elements, 3-micron, high-
-pressure SE filters are not normally replaced on a
prescribed periodic basis. Because of their large
dirt-holding capacity and nature of service, it is more
effective to replace such elements only when
indicated as being loaded by their associated
differential pressure indicators. Element replacement
procedures vary with the particular type, and
applicable maintenance instructions should be
consulted for specific procedures.
7 - 33