Screw extractors (view B) are straight, with
spiraling flutes at one end. These extractors are
available in sizes to remove broken screws having
1/4- to 1/2-inch outside diameters (ODs). Spiral tapered
extractors are sized to remove screws and bolts from
3/16 inch to 2 1/8 inches OD.
Most sets of extractors include twist drills and a
drill guide. Tap extractors are similar to the screw
extractors and are sized to remove taps ranging from
3/16 inch to 2 1/8 inches OD.
To remove a broken screw or tap with a spiral
extractor, first drill a hole of proper size in the screw or
tap. The size hole required for each screw extractor is
stamped on it. The extractor is then inserted in the hole,
and turned counterclockwise to remove the defective
component.
REVIEW QUESTIONS
Q36.
State the purpose of screw and tap extractors.
PIPE AND TUBING CUTTERS AND
FLARING TOOLS
LEARNING
OBJECTIVES:
State
the
purpose of pipe cutters, tube cutters, and
flaring tools.
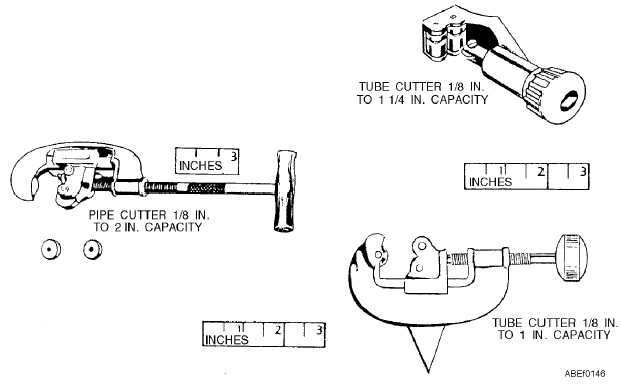
Pipe cutters (fig. 1-69) are used to cut pipe made of
steel, brass, copper, wrought iron, or lead. Tube cutters
(fig. 1-69) are used to cut tubing made of iron, steel,
brass, copper, or aluminum. The essential difference
between pipe and tubing is that tubing has considerably
thinner walls. Flaring tools (fig. 1-70) are used to make
flares in the ends of tubing.
Two sizes of hand pipe cutters are generally used in
the Navy. The No. 1 pipe cutter has a cutting capacity of
1/8 inch to 2 inches, and the No. 2 pipe cutter has a
cutting capacity of 2 to 4 inches. The pipe cutter (fig.
1-69) has a special alloy-steel cutting wheel and two
pressure rollers, which are adjusted and tightened by
turning the handle.
Most TUBE CUTTERS closely resemble pipe
cutters, except that they are of lighter construction. A
hand screw feed tubing cutter of 1/8-inch to 1 1/4-inch
capacity (fig. 1-69) has two rollers with cutouts located
off center so that cracked flares may be held in them
and cut off without waste of tubing. It also has a
retractable cutter blade, which is adjusted by turning a
knob. The other tube cutter shown is designed to cut
tubing up to and including 1 inch OD. Rotation of the
triangular portion of the tube cutter within the tubing
will eliminate any burrs.
FLARING TOOLS (fig. 1-70) are used to flare soft
copper, brass, or aluminum. The single flaring tool
consists of a split die block, which has holes for 3/16-,
1/4-, 5/16-, 3/8-, 7/16-, and 1/2-inch OD tubing; a
clamp to lock the tube in the die block; and a yoke,
1-43
Figure 1-69.—Pipe and tubing cutters.