CHAPTER 6
M61A1 GUN INSTALLATION
Gun systems installed in high-speed aircraft must
meet demanding performance requirements and
provide firepower. The General Electric M61A1
20-mm automatic gun system, installed in the F-14 and
F/A-18 aircraft, meets these requirements.
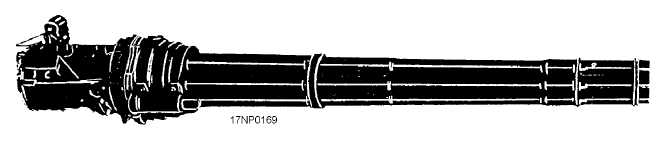
The M61A1 (fig. 6-1) is a six-barrel, rotary-action,
automatic gun based on the machine-gun design of
Richard J. Gatling. The gun consists of a revolving
cluster of barrels. Each barrel is fired once per
revolution. The M61A1 automatic gun is hydraulically
driven, electrically controlled, and can fire M50 and
PGU-series ammunition at 4,000 to 7,200 rounds per
minute. As installed in Navy aircraft, the gun has a pilot
selectable firing rate of either 4,000 (GUN LOW) or
6,000 (GUN HIGH) rounds per minute. It is designed
for either air-to-ground or air-to-air gunnery missions.
Ammunition is supplied to the M61A1 gun by an
ammunition handling and storage system that functions
within a specific aircraft. The system uses an endless
conveyor that transports 20-mm ammunition from the
ammunition drum to the gun. The conveyor then returns
the expended cases and unfired rounds to the
ammunition drum.
Although the physical location of components
varies between different aircraft gun installations, the
function and description of the components are
essentially the same.
M61A1 AUTOMATIC GUN
LEARNING
OBJECTIVE:
Identify
the
components of the M61A1 automatic gun and
recognize the operating principles.
The primary parts of the gun are the barrels,
housing assembly, and rotor assembly. The following
paragraphs
contain
a
description
of
each
gun
component and an explanation of how each component
works. Figure 6-2 shows an exploded view of the gun
components, and figure 6-3 shows the gun component
locations. As each component is discussed, you should
look at these figures.
GUN COMPONENTS
The primary parts of the gun are described in the
following paragraphs.
Muzzle clamp assembly. The muzzle clamp
assembly is positioned at the outer end of the barrels. It
restrains individual barrel movement during firing. It is
positioned against the flange on the barrels and secured
by the pressure of the self-locking nut assembly against
the opposite side of the shoulders.
Mid-barrel clamp assembly. The mid-barrel
clamp assembly is positioned near the center of the
barrels. The clamp tabs are engaged in the slots of the
stop shoulders on the barrels. Secure the clamp in this
position by rotating the locating disk to the locked
position. The direction of rotation of the gun and barrel
hue prevents the clamp from unlocking. Insert a cotter
pin through the locking disk and clamp plate as an
additional safety measure.
Barrels. The M61A1 automatic gun has six rifled
barrels. The stub rotor attached to the rotor body
supports them. The three rows of interrupted locking
lugs on the barrel engage similar interrupted locking
lugs in the rotor to secure the barrel. There are three
6-1
Figure 6-1.—M61A1 automatic gun.