Part per million is the reference for water
In addition to causing extra maintenance and
contamination. If you take a 32-ounce sample
engine failure, fuel contamination causes serious
bottle and fill it 3 1/4 inches from the bottom,
delays in flight operations. Contaminated fuel
you have about 500 cubic centimeters (cc).
must be tracked back to the source of contamina-
Break the 500 cc down into one million little
tion and the problem corrected. Until the cause
pieces. You now have 1ppm. Of course, you
of contamination is found and corrected, the
must use accurate surveillance equipment to
contaminated system cannot be used. The fuel
perform measurements that small. Normally,
system may be a mobile refueler, air station
the organizational maintenance level does not
hydrant refueling system, or the entire fuel system
require this precise testing and inspection.
of an aircraft carrier. Contaminated fuel could
Instead, the organizational level visually inspects
affect one aircraft or the operation of an entire
air wing.
fuel samples for contamination.
Measuring Contamination
Types and Limits of Contamination
How do you determine how much contamina-
Acceptable fuel is clean and bright with no
visually detected free water. The terms clean and
tion is too much? First, you have to understand
bright have no relation to the natural color of the
the units of measurements used to identify
fuel. Jet fuels are not dyed and vary from clear,
contamination. The two units for measuring
water white to straw-yellow in color. Clean means
contamination are microns for solids and parts
the absence of any cloud, emulsion, visible
per million (ppm) for water.
sediment, or free water. Bright means the fuel has
a shiny, sparkling appearance. A cloud, haze,
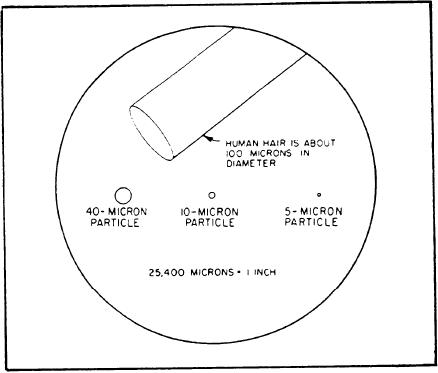
There are about 25,400 microns in 1 inch.
specks of particulate matter, or entrained water
Figure 4-2 gives you a microscopic view of
indicates contaminated fuel that cannot be used.
a human hair compared with small particle
Steps must be taken to find the source of
Figure 4-2.--Enlargement of small particles and comparison to human hair.
4-5

