Each operating activity participating in the
of that time specified. This requirement must be
NOAP must take routine samples properly
considered when equipment is scheduled for
and at the prescribed intervals. In addition to
detachments or missions away from the home
the routine samples, each operating activity is
base. Oil samples will still be due while away. The
required to submit special samples under the
customer (squadron or detachment) is responsible
following conditions:
for coordinating oil analysis support at mission
or transit site(s).
1. When samples are requested by the CFA
or by the laboratory.
NOTE: Refer to the applicable scheduled
maintenance or periodic inspection docu-
2. When the activity is so directed by the unit
ment for the specific routine sampling
maintenance officer to check out suspected
interval. Also look for specific sampling
deficiencies.
instructions for each type/model/series of
3. When abnormal conditions exist, such as
equipment being sampled.
malfunction of the oil lubricated part, damage to
the oil lubricating system, excessive engine oil loss,
or zero oil pressure.
4. Before and after the replacement of major
oil lubricating system parts.
5. During and at the completion of a test cell
run. If the repaired or suspect unit is operated on
oil previously used in the test cell system, a sample
must be taken. This is done before and after the
completion of the test cell run.
6. After the final test on an aircraft that is
undergoing rework or scheduled depot-level
maintenance or after installations of new/over-
hauled engines or engines repaired by AIMD.
7. Following all accidents, regardless of cause
and resulting damage. These samples must be
taken by any means possible to get a representative
sample.
There are two basic methods of taking a fluid
sample: (1) the dip tube technique, and (2) the
drain technique.
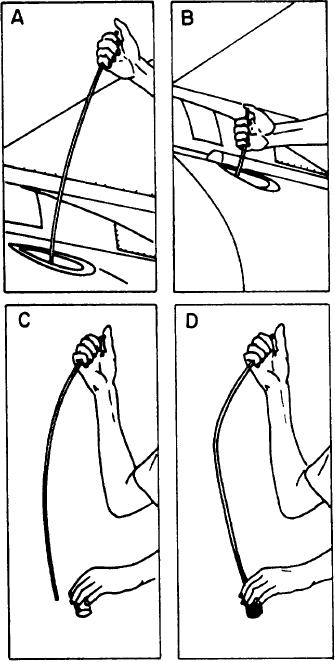
DIP TUBE SAMPLING.-- The following
procedures should be followed when using the dip
tube method for getting a fluid sample:
1. Remove the filler cap from the oil tank and
open the sample bottle.
2. Use a sampling tube of the correct length.
Hold the tube at one end and lower it into the
tank through the filler neck until only the upper
end protrudes. (See fig. 5-18, views A and B.)
3. Allow the lower end of the tube to fill with
oil, then close the upper end with your thumb or
finger. Withdraw the tube and drain the trapped
oil into the sample bottle. (See fig. 5-18, views
C and D.) Repeat this operation until the bottle
Figure 5-18.-Dip tube oil sampling.
5-23

