The power supply is self-contained. It is
pump, and lines. Eventually the stand will fail,
designed to check the performance and character-
either jamming or collapsing.
i s t i c s of aircraft hydraulic systems. The
B-2 Workstand
A/M27T-5 is capable of performing the follow-
ing functions:
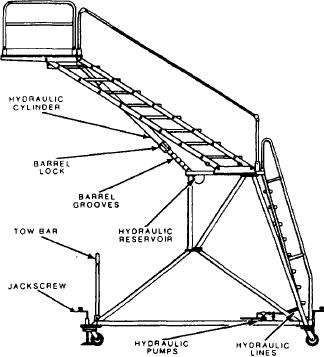
A type of workstand in common use is the B-2,
1. Delivering hydraulic fluid at controlled
shown in figure 3-15. The B-2 consists basically
pressures. This enables operation of the aircraft's
of a fixed height, 10-foot lower structure; a
hydraulic system without the need to start the air-
variable height upper structure; and a manual
craft's engines.
pump-actuated hydraulic system for raising and
2. Testing the flow rate of aircraft hydraulic
lowering the upper structure. The upper structure
systems.
includes a work platform with guardrails and steps
with handrails. The platform and steps, because
3. Testing the aircraft hydraulic system and
components for leakage or malfunction.
of parallelogram linkage, stay horizontal
4. Flushing and refilling aircraft hydraulic
throughout their upward or downward travel. The
systems with MIL-H-83282 hydraulic fluid filtered
lower structure includes fixed steps and handrails,
to 3-micron absolute.
a tow bar, and four free-swivel caster wheels for
mobility. Each caster is equipped with a safety
locking device containing a spring-loaded pin,
which snaps into notches on the caster pivot axle
NONPOWERED SUPPORT
EQUIPMENT
to lock the caster swivel. The lower structure also
includes four immobilizing jacks with baseplates.
So far we have discussed only powered SE.
The jack plates press against the ground and act
This portion of the text will discuss nonpowered
as brakes, but not supports, for the structure. You
may find some B-2 stands with the foot-lever
support equipment. Nonpowered SE is all the
brakes (like the B-4A and B-5A) instead of the
equipment that has no engine or motor installed
to supply power for equipment operation.
jackscrews.
The height range for the B-2 work platform
MAINTENANCE PLATFORMS
is from 13 feet to 20 feet. Overall height, including
the 3 1/2-foot guardrails, is 16 1/2 feet lowered
Maintenance stands, platforms, or workstands
(the names are commonly interchangeable) give
us a means to reach parts of the aircraft we can't
safely reach or work on from the ground. There
are a large variety of types and models. Some of
the stands are common SE used on almost any
type of aircraft. Others are very large stands used
only at shore activities or on one specific type of
aircraft.
Most adjustable aircraft maintenance plat-
forms are hydraulically operated. A platform and
ladder assembly are mounted on a caster-equipped
base. This enables maintenance personnel to safely
work at heights from 3 feet to a maximum of 20
feet, depending on the stand selected. Since the
design, use, safety precautions, and procedures
are generally very similar, we will cover only a
few of the more common stands.
Most maintenance workstands become de-
fective through abuse and lack of care. Most small
stands are designed to hold 500 pounds safely.
Overloading the stand can cause some part of the
platform structure to bend. That generally causes
the lift structure, or steps to bind. That, in turn,
Figure 3-15.-B-2 maintenance platform.
puts abnormal pressure on the hydraulic cylinder,
3-13

