TINNING --The process of applying a thin
STATOR --(l) The stationary part of a
coat of solder to materials prior to their being
rotating electrical machine. The stator may be
soldered; for example, application of a light coat
either the field or the armature, depending on the
of solder to the filaments of a conductor to hold
design of the machine. (2) The stationary member
the filaments in place prior to soldering of the
of a synchro that consists of a cylindrical structure
conductor.
of slotted laminations on which three Y-connected
coils are wound with their axes 120 degrees apart.
TORQUE --The turning effort or twist that
Depending on the type of synchro, the stator's
a shaft sustains when transmitting power. A force
functions are similar to the primary or secondary
tending to cause rotational motion; the product
windings of a transformer.
of the force applied times the distance from the
force to the axis of rotation.
STRANDED CONDUCTOR --A conductor
composed of a group of wires, The wires in a
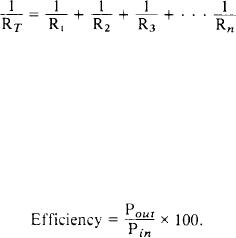
TOTAL RESISTANCE (RT) --The equivalent
stranded conductor are usually twisted together
resistance of an entire circuit, For a series circuit:
and not insulated from each other.
R T = R1 + R2 + R3 + . . . RN . For parallel
circuits:
STRANDS --Fine metallic filaments twisted
together to form a single wire.
SUBASSEMBLY --Consists of two or more
TRANSFORMER --A device composed of
parts that form a portion of an assembly or a unit.
two or more coils, linked by magnetic lines of
force, used to transfer energy from one circuit to
SUPPORT EQUIPMENT (SE) --All the
another.
equipment on the ground or ship needed to
support aircraft in a state of readiness for flight.
TRANSFORMER EFFICIENCY --The ratio
of output power to input powver, generally
SYNCHRO --A small motor-like analog
expressed as a percentage.
device that operates like a variable transformer
and is used primarily for the rapid and accurate
transmission of data among equipments and
stations.
TRANSFORMER, STEP-DOWN --A trans-
SYNCHRO SYSTEM --An electrical system
former constructed so that the number of turns
that gives remote indications or control by means
in the secondary winding is less than the number
of self-synchronizing motors.
of turns in the primary winding. This construction
will provide less voltage in the secondary circuit
TACHOMETER --An instrument for indi-
than in the primary circuit.
cating revolutions per minute.
TRANSFORMER, STEP-UP --A trans-
former constructed so that the number of turns
TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT --The
in the secondary winding is more than the number
amount of change of resistance in a material per
of turns in the primary winding. This construction
unit change in temperature.
will provide more voltage in the secondary circuit
than in the primary circuit.
TERTIARY WINDING --A third winding on
a transformer or magnetic amplifier that is used
TRUE BEARING --Angle between a target
as a second control winding.
and true north measured clockwise in the
horizontal plane.
THERMISTOR --A resistor that is used to
compensate for temperature variations in a circuit.
TRUE NORTH --Geographic north.
See also BOLOMETER.
TUMBLE (GYRO) --To subject a gyro to a
THERMOCOUPLE --A junction of two
torque so that it presents a precession violent
dissimilar metals that produces a voltage when
enough to cause the gyro rotor to spin end over
end.
heated.
AI-10

