aircraft structure to maintain cockpit pres-
surization. The system, using cooled engine
bleed air from the air-conditioning system,
inflates the canopy seal in response to
movement of the canopy locking linkage.
The system deflates the seal when the can-
opy is unlocked. There are many different
types/designs of pressure-maintaining seals
used on naval aircraft. The main difference
between canopy seal systems is the type
of canopy seal pressure regulator used, elec-
trical or mechanical. The F-14 inflatable
seal will be discussed in the following para-
graphs. The A-6 operates in a similar man-
ner, but will not be covered in detail here.
Refer to maintenance manuals for specifics.
SYSTEM OPERATION
The canopy seal pressure regulator receives
cooled engine bleed air, at approximately 80 psi,
from the service air heat exchanger. When
the canopy is closed and locked, the regulator
plunger is released; this opens the shutoff
valve. Air from the regulator inlet then flows
past the check valve and shutoff valve, through
the outlet port, and to the canopy inflatable
seal. As air pressure in the seal increases,
pressure buildup in the regulator chamber
moves the bellows seat away from the flange.
The interior of the bellows is vented to
ambient. When pressure in the seal reaches
25±5 psi above ambient, the bellows will
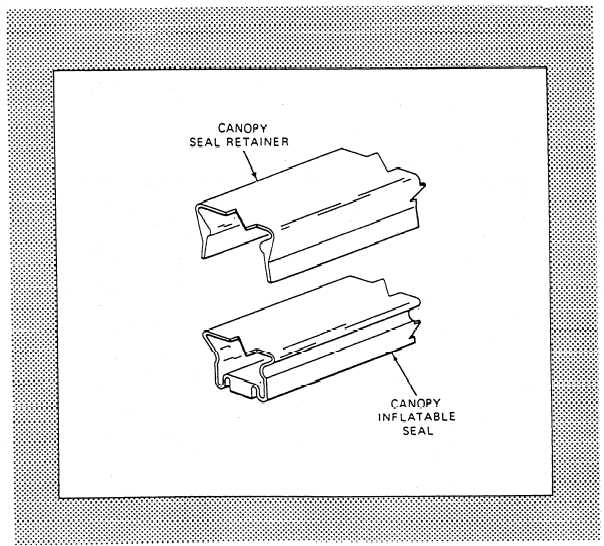
Figure 2-9.—Typical canopy inflatable seal (removed).
2-12