of the SUU-58/B dispenser, Mk 339 Mod 1 fuze, Kit
Modification Unit KMU-428/B, and 60 mines (45
BLU-91/B and 15 BLU-92/B). The fuze initiation
time is preset and is activated upon weapon release
from the aircraft. Fuze time settings are primary
mode (1.2 seconds) and option mode (4.0 seconds).
The KMU-428/B adapts the mines to the dispenser; it
also provides mine activation/self-destruct time
selection.
SUU-58/B Subsonic Free-Fall Dispenser
The SUU-58/B consists of a cargo section with a
nose fairing assembly attached, a tail cone assembly, and
fuze arming wires with extractors. There are two
observation windows-one for viewing the safe/arm
indicator and the other to observe the fuze time-setting
dials. The cargo section houses the BLU-91/B and
BLU-92/B mines. The tactical weapons have two
yellow bands around the nose cone fairing.
BLU-91/B and BLU-92/B Mines
The target sensors are the primary difference
between the two mines. The BLU-91/B uses an
armor-piercing warhead and a magnetometer type of
sensor; the BLU-92/B has a fragment type of warhead
with trip wires as the primary target sensor.
PRACTICE BOMBS
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: ldentify the
different types, purpose, and use of practice
bombs to include subcaliber and full-scale
practice bombs.
Practice bombs are used to simulate the same
ballistic properties of service bombs. Practice bombs
are manufactured as either solid, cast-metal bodies or
thin, sheet-metal containers. They can be filled with wet
sand to obtain the necessary weight. Since practice
bombs contain no explosive filler, a practice bomb
signal cartridge (smoke) can be used for visual
observation of weapon-target impact.
The primary purpose of practice bombs is safety
when training new or inexperienced pilots and
ground-handling crews. Other advantages of practice
bombs include their low cost and an increase in available
target locations.
Although not classified as practice bombs, the Mk
80 (series), inert filled, LDGP bombs are used for
full-scale practice bombing. These bombs are
physically the same as the Mk 80 (series) LDGP service
bombs, but they do not contain explosive filler and are
painted blue. These bombs provide full-scale training
for assembly and loading crews and pilots.
The general types of practice bombs are subcaliber
or full-scale practice bombs. Subcaliber means that the
practice bomb is much smaller in size and weight than
the service bomb it simulates. Full-scale practice
bombs are representative of service bombs in their size
and weight.
SUBCALIBER PRACTICE
BOMBS
There are two types of subcaliber practice
bombs-the Mk 76 Mod 5 and BDU-48/B. The two
types are used for practice and are quite different in
design and appearance from each other. Each type is
discussed in the following paragraphs.
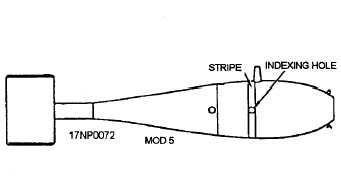
Mk 76 Mod 5
The Mk 76 Mod 5 is a 25-pound, solid, metal-cast,
practice bomb (fig. 1-41). Its body is teardrop shaped
and centrally bored to permit the insertion of a practice
bomb signal cartridge. The afterbody, which covers the
tail tube, is crimped to the bomb body and has welded-on
conical tail fins. The bomb is designed with single lug
suspension, using the Mk 14 suspension lug.
The Mk 76 Mod 5 practice bomb is designed for
impact firing only. It uses the Mk 1 firing pin assembly
to initiate the practice bomb signal cartridge. The bomb
signal and the firing pin assembly are held in the bomb
by means of a cotter pin.
The bomb is painted blue. The identification
nomenclature is stenciled in white letters on the bomb
body.
Figure 1-41.—Mk 76 Mod 5 practice bomb.
1-45