T46 (series) contains a fuze adapter sleeve for use with
the 1. 5-inch diameter fuze. A hole is drilled through the
threads of the primary adapter booster for insertion of a
locking pin for use with the long-delay fuze This pin
locks the adapter booster to the base plug of the bomb
and prevents removal of the adapter booster while the
fuze is installed. The M150 has a yellow band around
the adapter booster casing, which indicates that it is
loaded with explosives.
ELECTRICAL FUZES
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Identify the
various types of electrical fuzes to include their
physical description and functional operation.
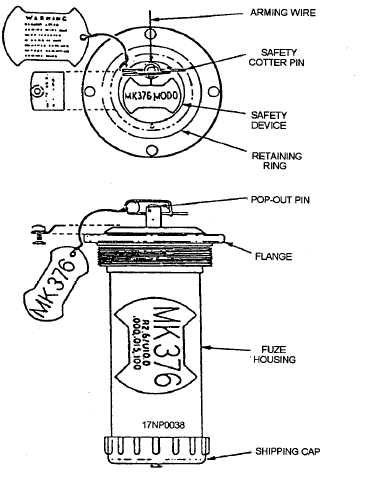
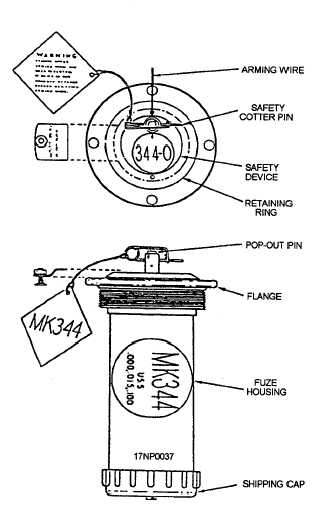
The Mk 344 (fig. 1-9) and Mk 376 (fig. 1-10)
electric bomb fuzes provide an all-electric capability for
the Mk 80 (series) bombs with either conical or retarding
fins, thermally protected bombs, and laser-guided
bombs (LGB). Electric fuzes require an electric pulse
from the aircraft fuze function control (FFC) system.
Figure 1-9.—Mk 344 Mods 0 and 1 electric fuzes.
Figure 1-10.—Mk 376 Mod 0 electric fuze.
The FFC gives in-flight selection of function delay and
arming delay times. The Mk 344 and 376 fuzes are used
with the Mk 43 target-detecting device for airburst
capability. They may also be used with mechanical nose
fuzes for additional fuzing options.
DESCRIPTION
The Mk 344 Mod 0 and Mod 1 and Mk 376 Mod 0
electric tail fuzes are detonator safe. The boosters
contain 4.3 ounces of tetryl explosive. They are
classified HERO SAFE, and no unusual RADHAZ
precautions are required under normal operating
conditions. The Mk 344 Mod 0 and Mod 1 fuzes are
identical, except that the retard sensor has been removed
from the Mod 1. The Mk 344 Mod 0 or Mod 1 is not
used in the retarded mode of delivery and should never
be configured for this type of delivery. The fuzes are
similar in appearance, but they are readily identifiable
by decals.
1-15