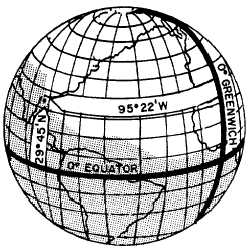
Figure 2-4.-Latitude is measured from the equator;
longitude from the prime meridian.
A position on the surface of the earth is expressed
in terms of latitude and longitude. Latitude is the
distance, either north or south, from the equator.
Longitude is the distance, either east or west, from the
prime meridian.
Distance
Distance as previously defined is measured by the
length of a line joining two points. In navigation, the
most common unit for measuring distance is the
nautical mile. For most practical navigation, all of the
following units are used interchangeably as the
equivalent of 1 nautical mile:
. 6,076.10 feet (nautical mile)
l One minute of arc of a great circle on a sphere
having an area equal to that of the earth
l 6,087.08 feet. One minute of arc on the earth’s
equator (geographic mile)
l One minute of arc on a meridian (1 minute of
latitude)
. Two thousand yards (for short distances)
It is sometimes necessary to convert nautical miles
into statute miles or statute miles into nautical miles.
This conversion is made with the following ratio
This means that 1 nautical mile equals 1.15 statute
miles.
The rate of change of position is determined by
speed. Speed is expressed in miles per hours, either
statute miles or nautical miles. If the measure of
distance is nautical miles, it is customary to use the
term knots. A speed of 200 nautical miles per hour
and a speed of 200 knots are the same. The phrase
“200 knots per hour” is incorrect unless you are
referring to acceleration.
Direction
Direction is the position of one point in space
relative to another without reference to the distance
between them. The time-honored system for
specifying direction as north, northwest, west, etc.,
does not meet the needs of modern navigation. A
numerical system meets the needs better for most
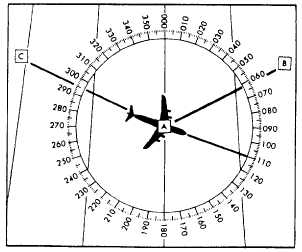
purposes. The numerical system (fig. 2-5) divides the
horizon into 360 degrees, starting with north as 000
degrees. Going clockwise, east is 090 degrees, south
180 degrees, west 270 degrees, and back to north.
The circle, called a compass rose, represents the
horizon divided into 360 degrees. The nearly vertical
lines represent the meridians, with the meridian of
position A passing through 000 degrees and
180 degrees. Position B lies at a true direction of 062
degrees from A, and position C is at a true direction of
295 degrees from A.
Determination of direction is one of the most
important parts of the navigator’s job. In order for the
navigator to accomplish this task, the various terms
involved must be clearly understood. Unless
otherwise stated, all directions are called true (T)
directions.
Figure 2-5.-Numerical system used in air navigation.
2-5