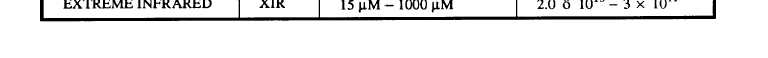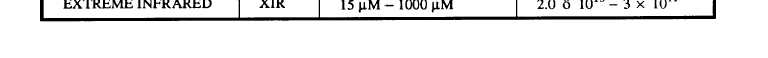Table 6-1.-Characteristics of IR Radiation
the target and the FLIR attenuates and blurs the target
signal. The FLIR operator aims the limited field of
view FLIR to search the scene for targets, using a
search pattern and clues, such as radar targets or laser
designators.
The FLIR system uses thermal sensitivity, image
sharpness, spectral response, contrast, and magnifi-
cation to produce a visual image of the thermal scene.
The operator uses training, experience, and image
interpretation skills to detect and identify targets.
INFRARED RADIATION
The atmosphere is a poor transmitter of infrared
radiation because of the absorption properties of CO2
(carbon dioxide), H2O (water), and 03 (ozone).
Infrared radiation is broken into four regions, as can
be seen in table 6-1. Only the first three are used with
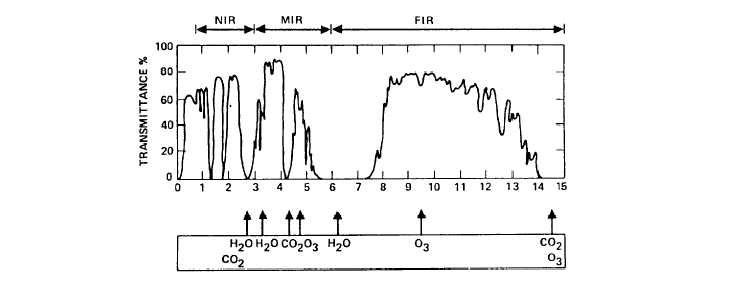
this system. Figure 6-3 shows the transmission
spectrum of the atmosphere. You can see that the best
transmission is between 3 µm and 5 pm, and between
8 µm and 14 µm.
The range between these
wavelengths is known as a window. Infrared imaging
devices are designed to operate in one of these two
windows, usually the 8 µm to 14 µm window.
Infrared Radiation Sources
All matter whose temperature is above -273°C
(absolute zero) emits IR radiation. The amount of the
radiation emitted is a function of heat. Theoretically,
a perfect emitter is a black body with an emissivity of
1. Realistically, the best emissivity is somewhere
around 0.98. The emissivity of various objects is
measured on a scale of 0 to 1.
Figure 6-3.-Transmission spectrum of the atmosphere.
6-3