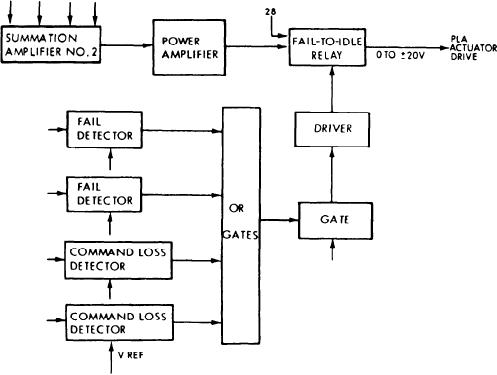
Figure 2-57.--PLA drive and fail-to-idle circuit.
Protective Functions
polarity of the signal is dependent on the shaft's
direction of rotation. The tachometer output
The protective functions of the PLA actuator
range is 0 to 2.7 volts dc nominal for a shaft
electronics are torque limit control, speed limit
input of 0 to 840 rpm.
control, acceleration limit control, PLA command
rate limit control, and system fail protection.
PLA Actuator Drive
TORQUE LIMIT CONTROL.--The PLA
actuator contains the circuitry that monitors for
The PLA actuator drive and fail-to-idle
an overtorque condition. Torque is calculated for
circuit (fig. 2-57) provides the power to drive the
either one or two engines in the operation on the
actuator motor. It also provides the fail-to-idle
FFGs or split plant or full power on the CG-,
signal that drives the motor during FSEE
and DD-class ships. If the torque signal
malfunctions.
received from the torque computer exceeds the
limit, the limiting circuit goes into action to
In normal operation, the output of summation
drive the MFC back, thereby reducing the torque
amplifier No. 2 is amplified by the power
output of the turbine(s).
amplifier in the power distribution assembly.
The output of this amplifier is sent through
SPEED LIMIT CONTROL.--The speed limit
the fail-to-idle relay. This signal, in turn,
control circuitry starts limiting when turbine speed
is sent to the PLA actuator. A fail-to-idle
reaches 3,672 rpm. The purpose of the speed limit
signal is sent to the relay from either the
control is to keep the turbine speed below 3,852
fail or command loss detector (discussed
rpm. The circuit receives a speed signal from the
under the system fail protection topic). If
signal conditioning card. This signal goes through
this occurs, the amplifier output is disconnected
an anticipation (to anticipate speed) amplifier; this
by the gate; a 28-volt dc signal is inserted
amplifier detects the rate of increase of the speed
to drive the motor. The polarity of this
(acceleration). This acceleration signal and the
signal is such that it drives the PLA to the
speed signal together are compared to a limit
idle stop.
2-54

