PROPERTIES OF DIESEL FUEL
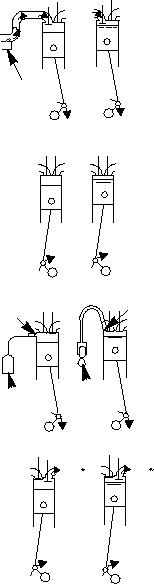
Figure 4-26 shows the comparison of the four
strokes of a 4-cycle diesel and a 4-cycle gasoline
Diesel fuel is heavier than gasoline because it is
engine.
obtained from the residue of the crude oil after the more
The speed of a diesel engine is controlled by the
volatile fuels have been removed. As with gasoline, the
amount of fuel injected into the cylinders; in a gasoline
efficiency of a diesel fuel varies with the type of engine
engine the speed of the engine is controlled by the
in which it is used. By distillation, cracking, and
amount of air admitted into the carburetor.
blending of several oils, a suitable diesel fuel can be
obtained for all engine operating conditions.
Mechanically, the diesel engine is similar to the
Slow-speed diesels use a wide variety of heavy fuels;
gasoline engine. The intake, compression, power, and
high-speed diesel engines require a lighter fuel. If you
exhaust strokes occur in the same order. The
use a poor or an improper grade of fuel, it can cause
arrangement of the pistons, connecting rods,
hard starting, incomplete combustion, a smoky exhaust,
crankshaft, and engine valves are about the same. The
and engine knocks.
diesel engine is also classified as inline or V-type.
The high injection pressures needed in the diesel
In comparison to the gasoline engine, the diesel
fuel system are made possible by close tolerances in the
engine produces more power per pound of fuel, is more
pumps and injectors. These tolerances make it
reliable, has lower fuel consumption per horsepower
necessary for the diesel fuel to have sufficient
per hour, and presents less of a fire hazard. These
lubrication qualities to prevent rapid wear or damage. It
advantages are partially offset by the high initial cost,
must also be clean, mix rapidly with the air, and burn
heavier construction needed for its high-compression
smoothly to produce an even thrust on the piston during
pressures, and the difficulty in starting, which results
combustion.
from these pressures.
DIESEL
GASOLINE
INTAKE STROKE
On downward stroke of piston,
On downward stroke of piston,
intake valve opens and atmos-
intake valve opens and atmos-
pheric pressure forces air
pheric pressure forces pure
through carburetor where it
air into the cylinder space
picks up a metered combustible
vacated by the piston; there
charge of fuel. The mixture
being no carburetor or throttle
goes past the throttle valve
valve. Cylinder fills with same
Into cylinder space vacated by
quantity of air, regardless of
CARBURETOR
the piston.
load on the engine.
COMPRESSION STROKE
On up stroke of piston, valves
On up stroke of piston, valves
are closed and mixture is com-
are closed and air is compressed
pressed, usually from 110 to 150
to 400 to 600 psi.
psi, depending on compression
ratio of engine.
POWER STROKE
NOZZLE
SPARK PLUG
High compression produces high
Compressed fuel-air mixture is
temperature for spontaneous
ignited by electric spark. Heat
ignition of fuel injected near
of combustion causes forceful
end of compression stroke.
expansion of cylinder gases
Heat of combustion expands
against piston, resulting in
FUEL
cylinder gases against piston,
power stroke.
MAGNETO
INJECTION
resulting in power stroke.
OR
PUMP
DISTRIBUTOR
900 F
1300 F
Up stroke of piston with exhaust
Up stroke of piston with exhaust
valve open forces burned gases
valve open forces burned gases
out, making ready for another
out, making ready for another
intake stroke.
intake stroke.
ASf04026
Figure 4-26.--Comparison of sequence of events in diesel and gasoline 4-cycle engines.
4-19

