Cold Fronts
A cold front occurs when cold air invades a region occupied by warm air.
Cold Front Characteristics
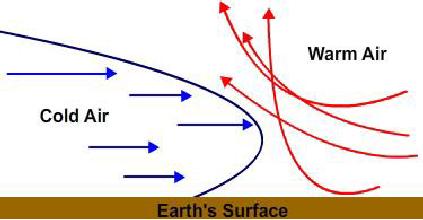
In a cold front, the cold air wedges under the warm air and pushes the warm air
upwards, as seen in Figure 1-6.
Figure 1-6 -- Cold front characteristics.
Certain weather characteristics and conditions are associated with the passage of cold
fronts. In general, the temperature and humidity decrease, pressure rises, and the wind
shifts clockwise in the northern hemisphere (clockwise movement on the wind direction
indicator, usually from southwest to northwest) with the passage of a cold front.
When the warm air mass is unstable and moist, showers and thunderstorms occur just
ahead of the front, and rapid clearing occurs behind the front. Squall lines and
tornadoes are associated with fast moving cold fronts.
When the warm air is relatively dry, a cold front may not produce precipitation or clouds.
Warm Fronts
A warm front occurs when cold air retreats before an advancing mass of warm air.
Warm Front Characteristics
With a warm front, the warm air slides over the cold air, as seen in Figure 1-7.
1-15

