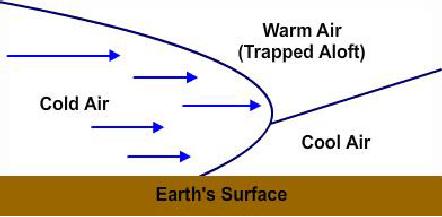
Occluded Front Characteristics
An occluded front can have the characteristics of both a warm front and a cold front
depending on the position of the front and the type of occluded front (warm or cold), as
seen in Figure 1-8.
Figure 1-8 -- Occluded front characteristics.
WEATHER HAZARDS
In this section, we will discuss some of the more serious weather hazards. A
comprehensive knowledge of these hazards and how they affect aircraft is essential to
providing good service. This knowledge also enables you to plan ahead and keep pilots
informed of known and anticipated weather conditions.
Fog and Precipitation
Fog is defined as a cloud on the earth's surface. It has sufficient density in the
atmosphere to interfere with visibility.
Fog consists of visible water droplets or ice particles suspended in the atmosphere. It
differs from other clouds in that it exists on the ground or over the surface of bodies of
water. It differs from rain or mist in that its water or ice particles are more minute and
are suspended (they do not fall earthward).
Fog Formation
The difference between the dew point (the temperature to which air, at constant
pressure, and water vapor content must be cooled for saturation to occur) and the
temperature is used to predict fog formation. The smaller the spread between the
temperature and the dew point the greater the possibility of fog formation. Dew point
depression is the term used to describe the difference, in degrees, between the two.
Fog seldom forms when the dew point depression is greater than 4 F.
1-17

