rockets, guided missiles, and underwater weapons used
by the Navy are discussed in the following text.
AIRBORNE ROCKETS
The Navy uses two types of rockets—the 2.75-inch
Mighty Mouse and the 5.0-inch Zuni. The 2.75
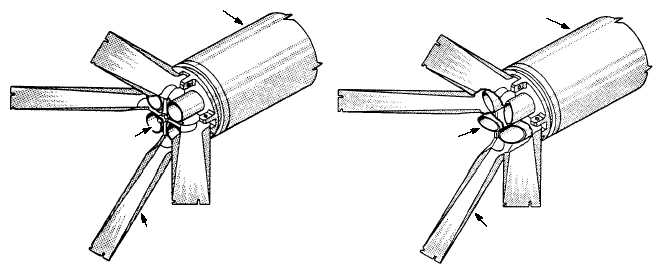
standard folding-fin aircraft rocket (FFAR) motor (fig.
8-8, view A) uses a standard nozzle insert. The
low-speed FFAR rocket motor (fig. 8-8, view B) uses a
scarfed nozzle insert. When the low-speed rocket is
fired, the scarfed nozzle insert causes the rocket to spin
during flight. This spin enables the rocket to be fired
from a slow-flying aircraft, such as a helicopter, and
still maintain trajectory to the target.
In early development, both the Mighty Mouse and
the Zuni were used against both air and ground targets.
However, with the introduction of modern missile
technology, rockets are now used primarily against
ground targets. The Mighty Mouse is fired in large
numbers. It is carried in rocket launchers with a
capacity of 7 or 19 rockets. The Zuni, which carries a
much larger explosive payload than the Mighty Mouse,
is carried in rocket launchers with a capacity of four
rockets. Both the Mighty Mouse and the Zuni are fired
either singularly, in pairs, or in ripple salvo.
AIR-LAUNCHED GUIDED MISSILES
A guided missile is defined as "a self-propelled
object that automatically alters its direction of flight in
response to signals received from outside sources."
Guided missiles are equipped for, and usually carry,
high-explosive charges. They have the means to
explode on contact or in near proximity of a target. The
majority of guided missiles used in the Navy are
essentially rockets that can maneuver while in flight
and make course corrections to intercept the target.
Guided missiles are classified according to their
range, speed, and launch environment, mission, and
vehicle type. Long-range guided missiles can usually
travel at least 100 miles. Short-range guided missiles
usually do not exceed the range capabilities of
long-range guns. Between these extremes the Navy has
an arsenal of medium or extended-range guided
missiles.
Guided missile speed is expressed in Mach
numbers. The Mach number "is the ratio of the speed of
an object to the speed of sound in the medium through
which the object is moving."
Therefore, an object
moving at sonic speed is traveling at Mach 1. In air
under standard atmospheric conditions, sonic speed is
766 miles per hour. Guided missiles are classified
according to speed as follows:
1. Subsonic—up to Mach 0.8,
2. Transonic—Mach 0.8 to Mach 1.2,
3. Supersonic—Mach 1.2 to Mach 5.0, and
4. Hypersonic—above Mach 5.0.
The speed of the launching aircraft is added to the speed
of the missile. Therefore, if a missile's speed is Mach
2.5 and the aircraft's speed, at the time of missile
launch, is Mach 2.0, the missile would be traveling at
Mach 4.5.
8-11
MOTOR TUBE
NOZZLE INSERT
FIN
STANDARD NOZZLE
FIN
SCARFED NOZZLE
NOZZLE INSERT
MOTOR TUBE
(A)
(B)
ANF0808
Figure 8-8.—Nozzle and fin assemblies. (A) standard nozzle; (B) scarfed nozzle.