AIRBORNE AUXILIARY POWER UNITS (APU)
Most larger aircraft use APUs. These power units
furnish electrical power when engine-driven generators
are not operating or when external power is not
available. The power output from the APU supplies a
constant voltage at a constant frequency. The APU does
not depend on engine rpm.
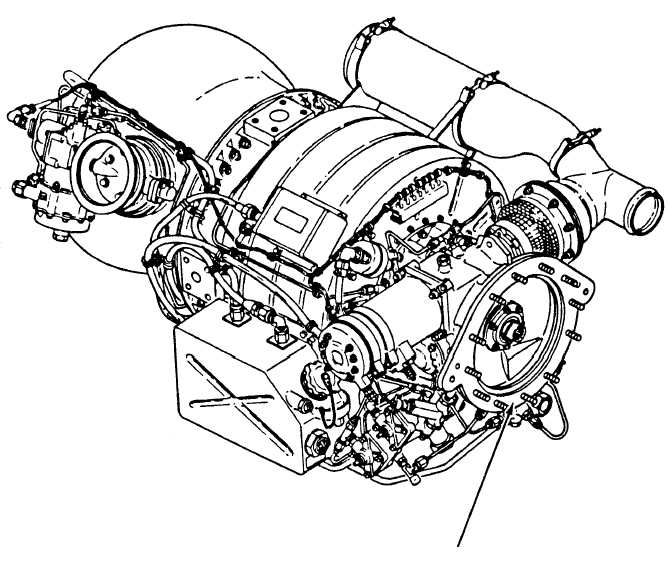
Most units use a gas turbine (fig. 7-3) to drive the
generator. The gas turbine provides compressed air for
air conditioning and pneumatic engine starting. This
makes the aircraft independent of the need for ground
power units to carry out its mission.
CARRIER AIRCRAFT ELECTRICAL POWER
SERVICING SYSTEM
The deck-edge electrical power system on aircraft
carriers provides servicing power to aircraft.
Twenty-eight volt dc power is supplied by rectified ac or
by motor-generators. Ac generators usually supply the
400-hertz, three-phase, ac servicing voltage. Figure 7-4
shows an electrical power service system found on
modern carriers. Power is supplied by service outlets
located at the edge of the flight deck or from recesses in
the flight deck. Additionally, receptacles are located
throughout the hanger bay. All systems have standard
remote control switches, service outlet boxes, and
7-4
APU GENERATOR
MOUNTING PAD
ANF0703
Figure 7-3.—Gas turbine power plant unit.