ALTERNATING CURRENT (AC)
SYSTEMS
LEARNING OBJECTIVES: Identify the
basic purpose and operating principles for
aircraft ac electrical systems. Identify the
purpose of gyroscopes. Identify navigational
instruments and recognize their purpose.
As you just learned, energy for operating most
electrical equipment in an aircraft depends primarily on
energy supplied by a generator. A generator converts
mechanical energy into electrical energy. Generators
that produce ac are called ac generators or alternators.
Most naval aircraft use ac electrical systems as the
primary source of power. Most equipment aboard is ac
powered. The few requirements that remain for direct
current (dc) are normally supplied by a system of
rectifiers. A rectifier converts ac power to dc power.
Auxiliary power units (APUs), discussed later in this
chapter, provide ground service and emergency power.
(See Navy Electricity and Electronics Training Series
(NEETS), Module 5, NAVEDTRA 172-05-00-79, for
detailed information on the construction and operation
of ac generators and motors. Module 5 also discusses
the principles of rectification and voltage regulation.)
EMERGENCY ELECTRICAL POWER
For many years, the storage battery was the only
source
of
emergency
electrical
power.
Recent
advancements in avionics equipment have caused
emergency electrical loads to exceed the capability of
storage batteries. Also, the aircraft storage battery with
its highly corrosive electrolyte damages precision
equipment and precious metals used in today's aircraft.
For these reasons, there are new methods of providing
emergency electrical power.
EMERGENCY POWER GENERATORS
Many jet aircraft have emergency generators.
These generators provide emergency electrical power
in the event of main electrical power failure.
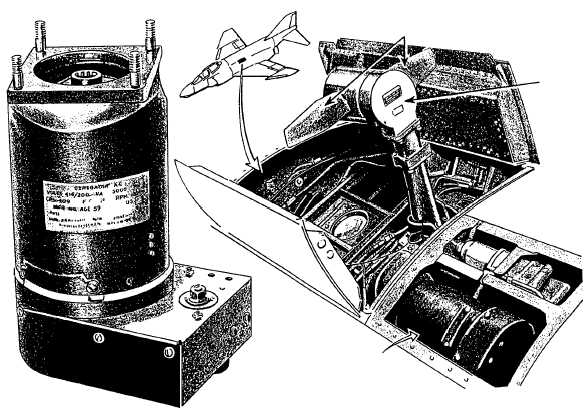
In some aircraft, a power package positioned out-
side the aircraft provides emergency electrical power.
When required, the pilot operates a lever that causes the
package to stick out into the airflow. The ram-air effect
of the airflow provides the turning power for a turbine.
The turbine, in turn, rotates the generator's armature
(fig. 7-2) that produces the electrical power.
7-3
EMERGENCY GENERATOR
TURBINE BLADES
DRIVE
UNIT
(B)
(A)
ANF0702
Figure 7-2.—(A) Emergency generator; (B) emergency generator installation.