end-for-end arrangement (plan B, fig. 2-5) requires the
least space per worker, and the single-desk arrangement
(plan A, fig. 2-5) requires the most. The best
arrangement is sometimes influenced by the
dimensions of the space as shown in plans D and E in
figure 2-5, Aisle space standards should range from 3
feet for secondary aisles to 8 feet for main corridors,
depending on the traffic.
The space requirements for filing cabinets depend
on the size of the cabinet, the frequent y of use of the
material filed, and the arrangement. The standard legal
file cabinet is 18- inches wide and 30-inches deep. The
drawer opens out an additional 28 inches. For inactive
or dead files, no additional aisle space is necessary. For
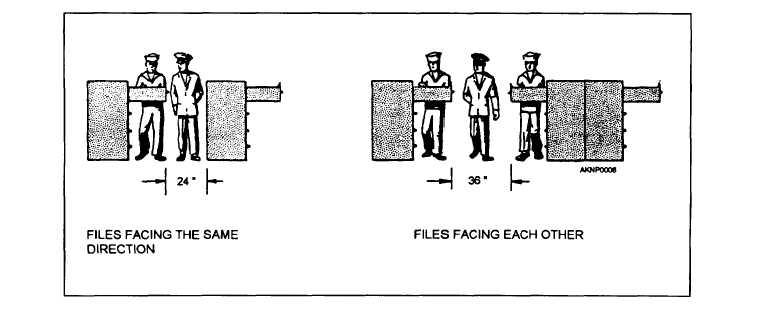
active files, 24 additional inches for the aisle are
required, or 36 inches if files are arranged facing each
other.
Figure 2-6 illustrates some common
arrangements of filing cabinets.
BULK STORAGE
The term bulk storage refers to the storage of
palletized or packaged item in large quantity of loads
per item. You will find this operation in areas dealing
with storage of dry goods, paper, or sonobuoys. The
operations in these areas usually require the use of
material handling equipment (MHE).
In the aviation community, most Aviation
Storekeepers work with retail store procedures in the
Aviation Support Division/Supply Support Center
(ASD/SSC). the AKs use the term bulk storage to
describe the location of any items that require material
handling equipment (MHE) during storage or issue.
These items include heavy, bulky, or irregular-shaped
material in crates or pallets.
The following text describes the bulk storage
procedures for storing items in large quantities.
Factors That Affect Bulk Storage
Some of the factors that you should consider in the
layout are described in the following text.
. Item stackability
l Honeycombing
l Inventory profile
l Quantity of storage
You should observe the principle of storage by
quantity when developing the stack layout plan. If the
stack layout is not planned before storing material, it
will result in wasted storage space or inaccessible stock.
Storing material by sequence (figure 2-7, view A) can
cause honeycombing and storing different material by
slot (figure 2-7, view B) may generate locked stock.
Figure 2-7, view C, illustrates the maximum use of
storage space by applying the space approach,
appropriate pallet racks, and a location system.
The objective in floor stacking is to maximize
access while minimizing aisle loss. The inventory
profile tells the number of items and the number of
pallets per item. This will enable you to determine the
need for short and deep rows of stock.
Figure 2-6.-Aisles space for filing cabinets.
2-10