Figure 2-28.—Sheet spring nut.
POINT-WRENCHING NUTS.—These nuts are
generally used where a nut with a high tensile length
is required. These nuts are installed with a small
socket wrench. They are usually self-locking.
SHEAR NUTS.—These nuts are designed for
use with devices such as drilled clevis bolts and
threaded taper pins that are normally subjected to
shearing stress only. They are usually self-locking.
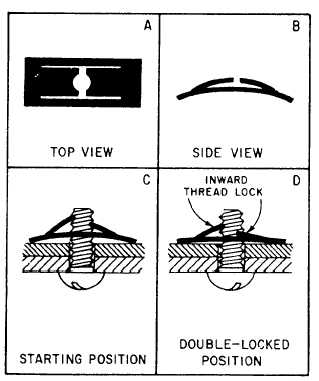
SHEET SPRING NUTS.—These nuts are used
with standard and sheet metal self-tapping screws to
support line clamps, conduit clamps, electrical
equipment, and access doors. The most common
types are the float, the two-lug anchor, and the
one-lug anchor. The nuts have an arched spring leek
that prevents the screw from working loose. They
should be used only where originally used in the
fabrication of the aircraft. See figure 2-28.
WING NUTS.—These nuts are used where the
desired tightness is obtained by the use of your fingers
and where the assembly is frequently removed.
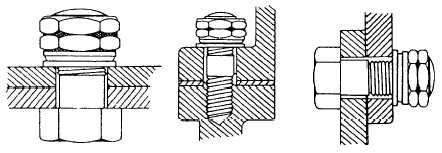
KLINCHER LOCKNUTS.—Klincher locknuts
are used to ensure a permanent and vibrationproof,
bolted connection that holds solidly and resists thread
wear. It will withstand extremely high or low
temperatures and exposure to lubricants, weather, and
compounds without impairing the effectiveness of the
locking element. The nut is installed with the end that
looks like a double washer toward the metal being
fastened. Notice in figure 2-29 that the end that looks
like a double hexagon is away from the metal being
fastened.
Screws
The most common threaded fastener used in
aircraft construction is the screw. The three most
used types are the structural screw, machine screw,
and the self-tapping screw.
STRUCTURAL SCREWS.—Structural screws
are used for assembling structural parts. They are
made of alloy steel and are heat treated. Structural
screws have a definite grip length and the same shear
and tensile strengths as the equivalent size bolt. They
differ from structural bolts only in the type of head.
These screws are available in round-head,
countersunk-head, and brazier-head types, either
Figure 2-29.—Typical installations of the Wincher locknut.
2-21