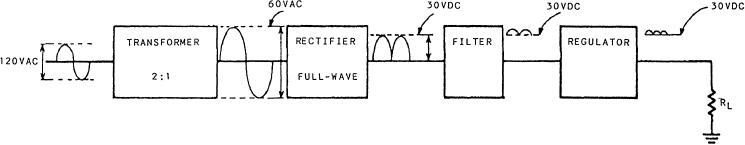
Figure 5-32.--Block diagram of a basic power supply.
The first section is the transformer. The transformer
volts dc to the load. You will read about voltage
regulators in the following sections.
serves two purposes: (1) to step up or step down the input
voltage to the desired level and (2) to couple this voltage
REGULATORS
to the rectifier section. The rectifier section is used to
convert the ac signal into a pulsating dc voltage.
The output of a power supply varies somewhat with
However, this pulsating dc voltage is not desirable and
changes in input voltage and circuit load current
must be smoothed. For this reason, the filter section is
requirements. The electronic consoles on gas turbine
used to convert the pulsating dc voltage into a filtered
ships require operating voltages and currents that
dc voltage. The final section, the regulator, does just
r e m a i n constant. For this reason, some form of
what its name implies. It maintains the output of the
regulation is needed. The circuits that maintain power
power supply at a constant level in spite of large changes
supply voltage or current outputs within specified limits,
in load current or in input line voltage. The output of the
or tolerances, are called regulators. They are designated
regulator will maintain a constant dc voltage within
either as dc voltage regulators or dc current regulators.
certain limits.
Now that you know what each section does, let's
Voltage Regulators
trace a signal through the basic power supply. You will
see what changes are made to the input signal as it passes
Voltage regulator circuits are additions to the basic
through each component of the power supply. Refer to
power supply circuits. The purpose of the voltage
figure 5-32 during this discussion.
regulator is to provide an output voltage with little or no
variation. Regulator circuits sense changes in output
The input signal of 120 volts ac is applied to the
voltages and compensate for the changes. Regulators
primary windings of the transformer. The transformer
that maintain voltage within plus or minus 0.1 percent
has a turns ratio of 2:1. The output of the step-down
are common.
transformer is calculated by dividing the input voltage
by the ratio of turns in the primary windings to the turns
Current Regulators
in the secondary windings. Therefore, 120 volts ac 2 =
60 volts ac at the output. Because the diodes in the
In most power supplies, current is not directly
rectifier section conduct only on the positive half of the
regulated. Fuses and other circuit protection devices are
input signal, the output will be only half of the input
used to set an upper limit to the amount of current that
signal. The output will be 30 volts of pulsating dc, sent
can flow in a power supply. Current is left unregulated
to the filter section of the power supply. The filter section
because the load will draw from the power supply only
contains a network of resistors, capacitors, or inductors.
the amount of current that it needs. Fluctuations in the
These components control the rise and fall time of the
power supply voltage caused by variations in load
varying signal so the signal remains at a more constant
current are usually controlled by the voltage regulator.
dc level. You can see that the output of the filter is at a
30-volt dc level with an ac RIPPLE voltage riding on it.
TROUBLESHOOTING
(Ripple voltage is a small ac voltage riding at some dc
voltage level. Normally, ripple voltage is an unwanted
Whenever you are working on the power supplies
ac voltage created by the filter section of a power
o f the ship's consoles, using the proper safety
supply.) The output signal from the filter goes to the
precautions is the most important thing you should
regulator. The regulator maintains a signal of about 30
remember. Always refer to the manufacturer's technical
5-41

