Motor-Operated Valves
the interior and exterior of the motor clean and free of
dirt. Remember, dirt and debris are the major causes of
motor failure.
Motor-operated valves allow the console operator
TROUBLESHOOTING.-- As a GSE, you must
remote control of certain valves in the ship's service fuel
troubleshoot the fuel booster pump motors whenever
system. Motor operators are found on the fuel service
tank suction and recirculating valves and fuel booster
malfunctions occur. A fault in the motor is usually
pump suction valves.
caused by short circuits, open circuits, or grounds. You
must locate and repair these faults to restore the fuel
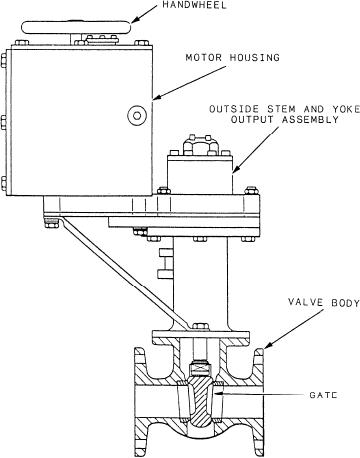
Study the motor-operated valve shown in figure 4-1.
The motor-operated valve assembly consists of an
system to its maximum operating condition. Refer to
electric motor driving a gear drive system that is coupled
chapter 5 for additional information on troubleshooting
to a valve. The motor housing contains a torque limiter
the fuel booster pump motors.
that protects the valve and the motor from overload
damage. Most types of motor-operated valves will also
Fuel Booster Pump Controllers
include a handwheel that permits manual operation if
electrical malfunction occurs. Motor-operated valves on
gas turbine-powered ships are remotely controlled from
On gas turbine-powered ships, the controllers for
the PCC, PACC, PLCC, and SCU, or locally at the valve
the fuel service system are located in the engine rooms.
controller.
The controllers operate from a 3-phase, 60-Hz, 440-volt
ac source and provide local control of the fuel booster
MAINTENANCE.-- The maintenance on motor-
operated valves includes cleaning, inspecting, and
pumps. The pumps can be stopped and started from
testing. The controller of a motor-operated valve is
these controllers. The controllers are usually equipped
nothing more than a simple reversing controller. The
with reset push buttons to restore motor overloads.
maintenance procedures used on motor-operated valves
M A I N T E N A N C E . The maintenance for the
are the same as those you would use to maintain basic
ship's service fuel booster pump controllers is the same
motors and controllers. On most gas turbine-powered
as for any other type of electrical controller. On most
gas turbine-powered ships, you, the GSE, will be
responsible for the maintenance of these controllers. On
some ships, however, this task may be the responsibility
of the electrician's mates (EMs).
In any case, proper preventive maintenance will
reduce the chance of failure in this equipment. Routine
PMS includes keeping the insulation resistance of the
control and power circuits high and making sure the
electrical connections are tight. Any problems you find
in the controllers must be corrected immediately. Make
sure you follow the proper electrical safety precautions
during the maintenance of these controllers.
TROUBLESHOOTING.-- During PMS on the fuel
booster pump controllers, you will sometimes find it
necessary to troubleshoot these devices. A fault in the
controller is usually caused by short circuits, open
c i r c u i t s , or grounds. Since the controller is an
electromechanical device, it will sometimes give in to
mechanical failure. You, the GSE, also must locate and
repair these types of faults to the controller. Refer to
chapter 5 for additional information on troubleshooting
Figure 4-1.--Fuel service system motor-operated valve.
fuel booster pump controllers.
4-2

