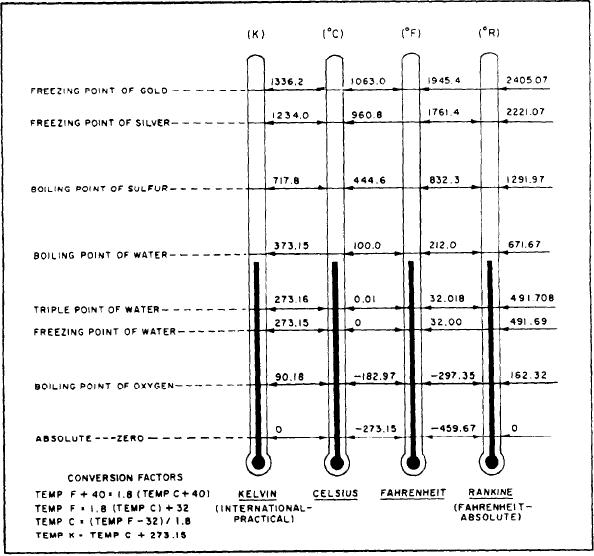
triple point of water, which is 0.01C above the
Degrees on the Rankine scale are the same size
freezing point of water, was chosen because it can
as degrees on the Fahrenheit scale, but the zero
be reproduced with much greater accuracy than
point on the Rankine scale is at -- 459.67
either the freezing point or the boiling point. On
Fahrenheit. In other words, absolute zero is zero
this new scale, the triple point was given the value
on the Rankine scale and -- 459.67 on the
273.16 K. Note that neither the word degrees nor
Fahrenheit scale.
the symbol is used; instead, the units are
A second absolute scale, the Kelvin, is more
referred to as Kelvin and the symbol K is used
widely used than the Rankine. The Kelvin scale
rather than the symbol K.
was originally conceived as an extension of the
In 1960 the triple point of water was finally
Celsius scale, with degrees of the same size but
adopted as the fundamental reference for this
with the zero point shifted to absolute zero.
temperature scale. The scale now in use is the
Absolute zero on the Celsius scale is -- 273.15.
international Practical Temperature Scale of 1968
In 1954, a new international absolute scale was
(IPTS-68). However, you often see this scale
developed. The new scale was based upon one
referred to as the Kelvin scale.
fixed point, rather than two. The one fixed point
Although the triple point of water is
was the triple point of water --that is, the point
considered the basic or fundamental reference for
at which all three phases of water (solid, liquid,
the IPTS-68, five other fixed points are used to
and vapor) can exist together in equilibrium. The
Figure 4-18.--Comparison of Kelvin, Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine temperatures.
4-18

