help define the scale. These are the freezing point
of pressure being measured under any given
of gold, the freezing point of silver, the boiling
conditions. To clarify the numerous meanings of
point of sulfur, the boiling point of water, and
the word pressure, the relationships among gauge,
the boiling point of oxygen.
atmospheric, vacuum, and absolute pressures, are
Figure 4-18 is a comparison of the Kelvin,
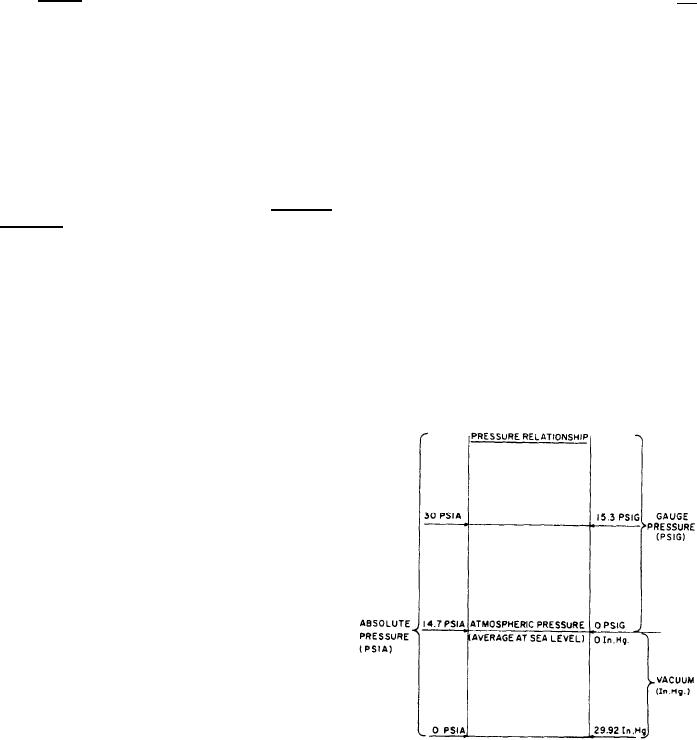
shown in figure 4-19.
Celsius, Fahrenheit, and Rankine temperatures.
GAUGE PRESSURE is the pressure actually
All of the temperature points listed above absolute
shown on the dial of a gauge that registers
zero are considered as fixed points on the Kelvin
pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. An
scale except for the freezing point of water. The
ordinary pressure gauge reading of zero does not
other scales are based on the freezing and boiling
mean that there is no pressure in the absolute
points of water.
sense; rather, it means that there is no pressure
in excess of atmospheric pressure.
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE is the pressure
PRESSURE DEFINITIONS
exerted by the weight of the atmosphere. At sea
level, the average pressure of the atmosphere is
Pressure like temperature is one of the basic
sufficient to hold a column of mercury at the
engineering measurements and one that must be
height of 76 centimeters or 29.92 inches. Since a
frequently monitored aboard ship. As with
column of mercury 1 inch high exerts a pressure
temperature readings, pressure readings provide
of 0.49 pound per square inch at its base, a
you with an indication of the operating condition
column of mercury 29.92 inches high exerts a
of equipment. Pressure is defined as the force per
pressure that is equal to 29.92 0.49 or about 14.7
unit area.
psi. Since we are dealing now in absolute pressure,
The simplest pressure units are the ones that
we say that the average atmospheric pressure at
indicate how much force is applied to an area of
sea level is 14.7 pounds per square inch absolute
a certain size. These units include pounds per
(psia). It is zero on the ordinary pressure gauge.
square inch, pounds per square foot, ounces per
square inch, newtons per square millimeter, and
Notice, however, that the figure of 14.7 psia
dynes per square centimeter, depending upon the
represents the average atmospheric pressure at sea
system you use.
level; it does not always represent the actual
You also use another kind of pressure unit that
pressure being exerted by the atmosphere at the
involves length. These units include inches of
moment that a gauge is being read.
water, inches of mercury (Hg), and inches of some
other liquid of a known density. Actually, these
units do not involve length as a fundamental
dimension. Rather, length is taken as a measure
of force or weight. For example, a reading of I
inch of water (1 in. H20 means that the exerted
pressure is able to support a column of water 1
inch high, or that a column of water in a U-tube
would be displaced 1 inch by the pressure being
measured. Similarly, a reading of 12 inches of
mercury (12 in.Hg) means that the measured
pressure is sufficient to support a column of
mercury 12 inches high. What is really being
expressed (even though it is not mentioned in the
pressure unit) is that a certain quantity of material
(water, mercury, and so on) of known density
exerts a certain definite force upon a specified
area. Pressure is still force per unit area, even if
the pressure unit refers to inches of some liquid.
In interpreting pressure measurements, a great
deal of confusion arises because the zero point
on most pressure gauges represents atmospheric
pressure rather than zero absolute pressure.
Figure 4-19.--Relationships among gauge pressure, atmos-
Thus it is often necessary to specify the kind
pheric pressure, vacuum, and absolute pressure.
4-19

