RTDs provide for remote readout of each bear-
ing's temperature on the digital demand displays.
Strut Bearings
Each propeller shaft extending aft of the stern
tubes is supported by a strut. Each strut contains
a seawater-lubricated bearing. The strut bearings
are cooled by constant immersion in seawater and
are not monitored by the ECSS.
Stern Tube Bearings
The stern tube bearings are in constant
contact with the seawater surrounding the stern
tubes. The clean seawater that passes through the
stern tube seals from the ship's firemain system
or seawater service system also flows through the
stern tube bearings. They are identical to the strut
bearings in design. However, the strut bearings
Figure 8-28.--Cross-sectional view of propulsion shaft.
are roughly 5-inches larger in diameter and twice
as long as the stern tube bearings. The stern tube
bearings are not monitored.
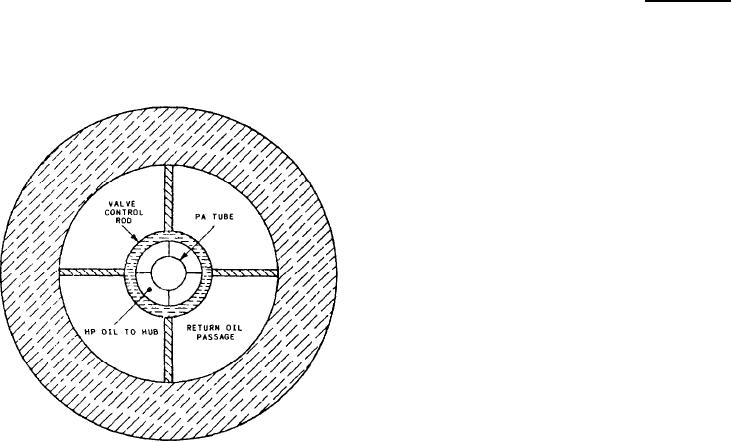
space between the valve rod and the inside
diameter of the propulsion shaft. It then flows
through the OD box to the hydraulic oil sump
PROPULSION SHAFT SEALS
tank.
The propulsion shaft penetrates the hull and
various compartment bulkheads. At these points
SHAFT BEARINGS
it is necessary to install some type of sealing
arrangement to prevent progressive flooding
The shaft bearings are used to support the
b e t w e e n compartments. Where the shaft
shaft. Bearings are mounted in the stern tube and
penetrates a compartment bulkhead, they are
propeller strut and are seawater lubricated. The
naturally called bulkhead seals. Where the shaft
remaining bearings are self-aligning, oil-lubricated
penetrates the hull, they are called stern tube seals.
journal bearings commonly called line shaft bear-
ings (LSBs). Each LSB is a self-contained
assembly with its own oil reservoir that contains
Bulkhead Seals
2190 TEP oil.
The bulkhead seals will maintain watertight
An oil disc clamped to the shaft is used in each
integrity of the bulkhead penetrated by shafting
when either side of the bulkhead is flooded. These
bearing to deliver oil to the upper bearing and
seals are self-aligned with the shaft. They will
journal surfaces. As the disc rotates, it picks up
oil from the bearing reservoir and carries it to the
accommodate 1.75 inches perpendicular move-
ment of the shaft with longitudinal movement of
oil scraper on the upper shell. The scraper removes
0.040 inches because of thrust bearing clearance
oil from the disc and directs it to the upper bear-
and 0.50 inch because of thermal changes.
ing lining. A clear sight hole cover on the bear-
ing housing allows visual confirmation of the oil
The seal assembly consists of a base
level and oil disc operation.
ring bolted to the bulkhead, two sealing
discs, right-hand and left-hand sealing rings,
and a cover. The two sealing rings are identical,
All bearing pedestals have an oil level rod and
except that one is a mirror image of the
an oil reservoir thermometer for checking oil level
other. They are formed by three plain and
and temperature. An RTD is installed in the lower
bearing shell of each oil-lubricated bearing. The
three slotted carbon segments. Six pressure ring
8-45

