that electrons may be removed from their parent
atoms and set in motion by energy derived from
a source of magnetism, friction, pressure, heat,
or light. In general, these forms of energy do not
alter the molecules of the substance being acted
upon. That is, molecules are not usually added,
taken away, or split up when subjected to these
four forms of energy. Only electrons are involved.
When the molecules of a substance are altered,
the action is referred to as CHEMICAL. For
instance, if the molecules of a substance combines
with atoms of another substance, or gives up
atoms of its own, the action is chemical in nature.
Such action always changes the chemical name
and characteristics of the substance affected. For
instance, when atoms of oxygen from the air come
in contact with bare iron, they merge with the
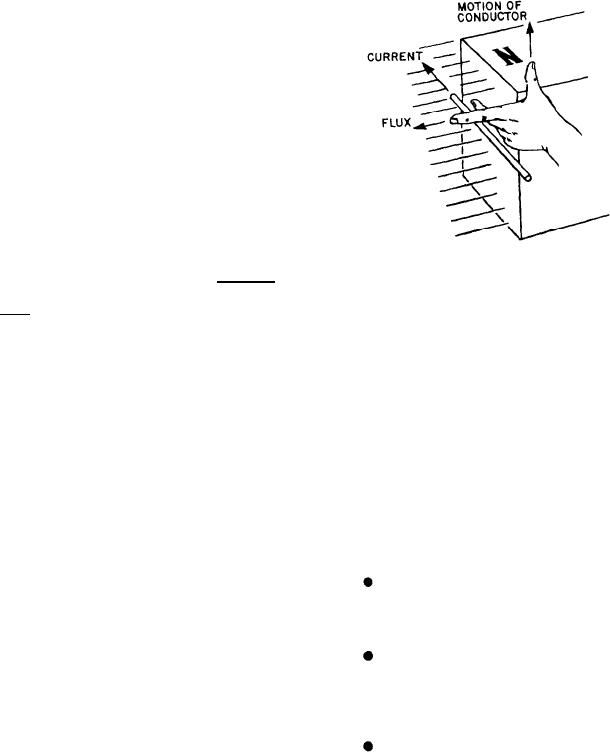
Figure 4-8.--Left-hand rule for generators.
molecules of iron. This iron is oxidized. It
has changed chemically from iron to iron oxide,
or rust. Its molecules have been altered by
MECHANICAL THEORY
chemical action.
In some cases, when atoms are added to or
To understand basic mechanical theory, you
taken away from the molecules of a substance,
must be familiar with the physics concepts used.
the chemical change will cause the substance to
In the following paragraphs we will discuss some
take on an electric charge. The process of
of the laws and principles that will enable you to
producing a voltage by chemical action is used in
better understand these concepts.
batteries.
LAWS AND PRINCIPLES
Left-Hand Rule For Generators
In this section we will first define, and then
In the preceding section we gave you a basic
explain, the basic laws and principles of
overview of voltage generation. This section will
mechanical theory.
explain and demonstrate the left-hand rule for
generators.
CHARLES'S LAW: If the pressure is
The left-hand rule for generators is a good
constant, the volume of an enclosed dry gas varies
representation of the relationships between
directly with the absolute temperature.
motion, magnetic force, and resultant current in
the generation of a voltage. By using this rule,
BOYLE'S LAW: The volume of an
you may find any of the three quantities if the
enclosed gas varies inversely with the applied
other two are known. This rule is explained in the
pressure, provided the temperature remains
following manner.
constant.
Extend the thumb, forefinger, and middle
finger of your left hand at right angles to one
another, as shown in figure 4-8. Point your thumb
NEWTON'S LAWS: The first law states
in the direction the conductor is being moved.
that a body at rest tends to remain at rest. A body
Point your forefinger in the direction of magnetic
in motion tends to remain in motion. The second
flux (from north to south). Your middle finger
law states that an imbalance of force on a body
will then point in the direction of current flow in
tends to produce an acceleration in the direction
an external circuit to which the voltage is applied.
of the force. The acceleration, if any, is directly
proportional to the force and inversely pro-
The more complex aspects of power genera-
portional to the mass of the body. Newton's third
tion by use of mechanical motion and magnetism
law states that for every action there is an equal
are discussed indepth in module 5 of the NEETS
and opposite reaction.
series.
4-8

