measured in inches outboard from that point, as shown
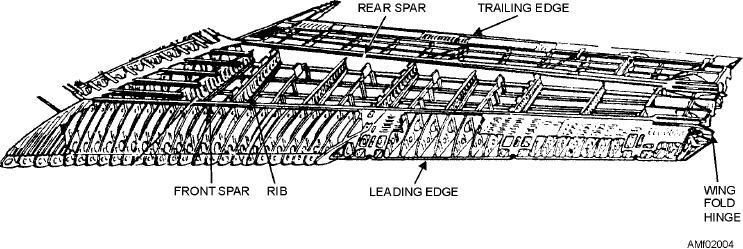
One method of wing construction is shown in
in figure 2-2.
figure 2-4. In this illustration, two main spars are used
with ribs placed at frequent intervals between the spars
Stabilizers
to develop the wing contour. This is called "two-spar"
construction. Other variations of wing construction
The stabilizing surfaces of an aircraft consist of
include "monospar (open spar), multispar (three or
vertical and horizontal airfoils. These are known as the
more spars), and box beam." In the box beam
vertical stabilizer (or fin) and the horizontal stabilizer.
construction, the stringers and sparlike sections are
These two airfoils, together with the rudder and
joined together in a box-shaped beam. Then the
elevators, form the tail section. For inspection and
remainder of the wing is constructed around the box.
maintenance purposes, the entire tail section is
The skin is attached to all the structural members
considered a single unit of the airframe, and is referred
and carries part of the wing loads and stresses. During
to as the "empennage."
flight, the loads imposed on the wing structure act
The primary purpose of the stabilizers is to stabilize
primarily on the skin. From the skin, the loads are
the aircraft in flight, that is, to keep the aircraft in
transmitted to the ribs and then to the spars. The spars
straight and level flight. The vertical stabilizer
support all distributed loads as well concentrated
maintains the stability of the aircraft about its vertical
weights, such as a fuselage, landing gear, and nacelle.
axis. This is known as "directional stability." The
Corrugated sheet aluminum alloy is often used as a
vertical stabilizer usually serves as the base to which
subcovering for wing structures. The Lockheed P-3
the rudder is attached. The horizontal stabilizer
Orion wing is an example of this type of construction.
provides stability of the aircraft about the lateral axis.
Inspection and access panels are usually provided
This is "longitudinal stability." It usually serves as the
on the lower surface of a wing. Drain holes are also
base to which the elevators are attached.
placed in the lower surfaces. Walkways are provided on
At high speeds, forces acting upon the flight
the areas of the wing where personnel should walk or
controls increase, and control of the aircraft becomes
step. The substructure is stiffened or reinforced in the
difficult. This problem can be solved through the use of
vicinity of the walkways to take such loads. Walkways
power-operated or power-boosted flight control
are usually covered with a nonskid surface. Some
systems. These power systems make it possible for the
aircraft have no built-in walkways. In these cases
pilot to apply more pressure to the control surface
removable mats or covers are used to protect the
against the air loads. By changing the angle of attack of
wing surface. On some aircraft, jacking points are
the stabilizer, the pilot maintains adequate longitudinal
provided on the underside of each wing. The jacking
control by rotating the entire horizontal stabilizer
points may also be used as tiedown fittings for securing
surface.
the aircraft.
Construction features of the stabilizers are in many
Various points on the wing are located by station
respects identical to those of the wings. They are
number. Wing station 0 (zero) is located at the
usually of an all-metal construction and of the
centerline of the fuselage. All wing stations are
Figure 2-4.--Typical wing construction.
2-4

