produced by combining carbon with other elements
ALLOYING OF METALS
known to improve the properties of steel. A base metal
A substance that possesses metallic properties and
(such as iron) to which small quantities of other metals
is composed of two or more chemical elements, of
have been added is called an alloy. The addition of other
which at least one is a metal, is called an "alloy." The
metals is to change or improve the chemical or physical
metal present in the alloy in the largest proportion is
properties of the base metal.
called the "base metal." All other metals and/or
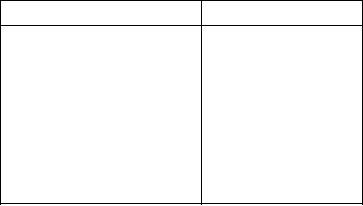
SAE NUMERICAL INDEX.--The steel
elements added to the alloy are called "alloying
classification of the Society of Automotive Engineers
elements." The metals are dissolved in each other while
(SAE) is used in specifications for all high-grade steels
molten, and they do not separate into layers when the
used in automotive and aircraft construction. A
solution solidifies. Practically all the metals used in
numerical index system identifies the composition of
aircraft are made up of a number of alloying elements.
SAE steels. Each SAE number consists of a group of
Alloying elements, either in small or in large
digits, the first of which represents the type of steel; the
amounts, may result in a marked change in the
second, the percentage of the principal alloying
properties of the base metal. For example, pure
element; and usually the last two or three digits, the
aluminum is a relatively soft and weak metal, but by
percentage, in hundredths of 1 percent, of carbon in the
adding small amounts of other elements such as copper,
alloy. For example, the SAE number 4150 indicates a
manganese, magnesium, and zinc, its strength can be
molybdenum steel containing 1 percent molybdenum
increased many times. Aluminum containing such
and 50 hundredths of 1 percent of carbon. Refer to the
other elements purposely added during manufacture is
SAE numerical index, shown in table 2-1, to see how
called an aluminum alloy.
the various types of steel are classified into four-digit
classification numbers.
In addition to increasing the strength, alloying may
change the heat-resistant qualities of a metal, its
Table 2-1.--SAE Numerical Index
corrosion resistance, electrical conductivity, or
Type of steel
Classification
magnetic properties. It may cause an increase or
decrease in the degree to which hardening occurs after
1xxx
Carbon
cold-working. Alloying may also make possible an
2xxx
Nickel
increase or decrease in strength and hardness by heat
3xxx
Nickel-chromium
treatment. Alloys are of great importance to the aircraft
4xxx
Molybdenum
industry in providing materials with properties that
5xxx
Chromium
pure metals alone do not possess.
6xxx
Chromium-vanadium
7xxx
Tungsten
FERROUS AIRCRAFT METALS
Silicon-manganese
9xxx
Many types of materials are required in the repair
of aircraft. This is a result of the varying needs with
HARDNESS TESTING METHODS.-- Hard-
respect to strength, weight, durability, and resistance to
ness testing is a factor in the determination of the results
deterioration of specific structures or parts. In addition,
of heat treatment as well as the condition of the metal
the particular shape or form of the material plays an
before heat treatment. There are two commonly used
important role. In selecting materials for aircraft repair,
methods of hardness testing, the Brinell and the
these factors, plus many others, are considered in
Rockwell tests. These tests require the use of specific
relation to their mechanical and physical properties.
machines and are covered later in this chapter. An
Among the common materials used are ferrous metals.
additional, and somewhat indirect, method known as
The term ferrous applies to the group of metals having
spark testing is used in identifying ferrous metals. This
iron as their principal constituent.
type of identification gives an indication of the
hardness of the metal.
Identification
Spark testing is a common means of identifying
ferrous metals that have become mixed. In this test, the
If carbon is added to iron, in percentages ranging
piece of iron or steel is held against a revolving stone,
up to approximately 1.00 percent, the product will be
and the metal is identified by the sparks thrown off.
vastly superior to iron alone and is classified as carbon
Each ferrous metal has its own peculiar spark
steel. Carbon steel forms the base of those alloy steels
2-26

