Quick-Disconnects
view A). As the weight travels downward, it further
depresses the valve assembly, forcing the demand valve
The anti-g suit is connected to the anti-g system
from its seat, thus overriding the pressure of the lower
by means of a quick-disconnect coupling. This
spring and opening the demand valve. Air pressure then
quick-disconnect may be either a single unit that
flows past the open demand valve, through the valve
connects the anti-g suit only, or it may be a composite
outlet into the valve outlet line, through the suit
quick-disconnect that connects the pilot to the various
quick-disconnect, and into the anti-g suit.
personal service lines (oxygen, ventilating air, anti-g
As the g-forces being applied to the aircraft are
system, and communications).
stabilized and become constant, the pressure under the
The anti-g system quick-disconnect is used on
activating weight diaphragm builds up sufficiently to
aircraft that are not equipped with a composite
lift the weight and to reduce the pressure on the valve
quick-disconnect attached to the ejection seat. This
assembly enough to close the demand valve (fig. 5-14,
disconnect is on a hose that protrudes through the
view B). The demand valve closes under pressure of the
pilot's console. It is attached by a flexible hose to the
heaver lower spring, while the exhaust valve remains
outlet port of the anti-g valve. This disconnect may be
closed by the activating weight. The suit pressure is
pulled up to a bumper stop to aid in connecting the
then trapped in the pressure outlet chamber of the anti-g
anti-g suit hose. A spring-loaded cover on the
valve and remains constant until the g-forces change.
disconnect prevents the entry of foreign material when
As the g-forces decrease, the downward force on
the system is not in use.
the activating weight diminishes to a point at which the
upper spring lifts the weight off the exhaust valve. The
OPERATION
pressure in the suit is then vented through the exhaust
port (fig. 5-14, view C) into the cockpit.
As high-g conditions occur, the anti-g valves
activating weight is forced down to close the exhaust
Pressing the button at the top of the valve manually
valve and open the demand valve. This allows cooled
operates the anti-g valve. This button should be used to
engine bleed air from the refrigeration system service
test the anti-g system prior to takeoff. Intermittent
heat exchanger to flow through the anti-g valve, where
manual operation of the anti-g valve is performed
it is regulated, to inflate the g-suit. Pressure to the g-suit
during flight to relieve leg stiffness and static fatigue.
is varied in proportion to the g-force acting upon the
aircraft and crewmembers, to a maximum of 10 psi. As
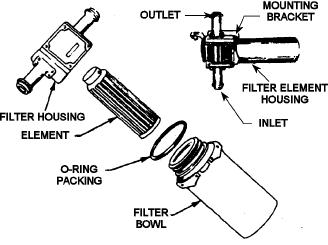
Anti-G System Filter
g-forces decrease, the activating weight is forced
upward by spring tension. This reduces the pressure of
Most anti-g systems use a filter to prevent particles
the airflow to the g-suit and exhausts excess suit
of dust, trash, and other foreign material from entering
pressure into the cabin. As this occurs, the demand
the regulating valve. This filter may be located in the
valve closes, blocking air from the g-suit.
supply line or it may attach to the anti-g valve on the
inlet side. A typical anti-g system filter is shown in
Q5-19.
Identify the purpose of an anti-g system.
figure 5-15.
Q5-20.
Most anti-g systems consist of what compo-
nents?
Q5-21.
The anti-g valve regulates high-pressure
bleed air to what maximum pressure for
delivery to the g-suit?
Q5-22.
Describe the operation of an anti-g system.
VENT-AIR SYSTEM
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Recognize the
components and operating principles for a
vent-air system.
Vent-air systems provide a flow of air to the
aircraft's seat or back cushions or to the ventilating air
Figure 5-15.--Anti-g system filter.
5-14

