0
ROTOR
ROTOR
LOOP
LOOPS
STATOR
120
240
ASfO6018
Figure 6-18.--A basic alternator with six pairs of poles in the
STATOR
rotor.
ASfO6019
Figure 6-19.--A three-phase alternator.
reactance) of the stator windings. The formula for
and L = inductance. As the speed of the rotor increases,
CROSS
the frequency of the output also increases. And, as the
SECTION
frequency increases, so does the impedance of the
stator coils. Eventually, the stator impedance increases
sufficiently to limit the output current.
Rectifiers
The battery and other electrical accessories in the
automotive electrical system operate on current that
flows in one direction only (direct current). For this
reason it is necessary to change the alternating current
ASf06020
to direct current. This function is performed by
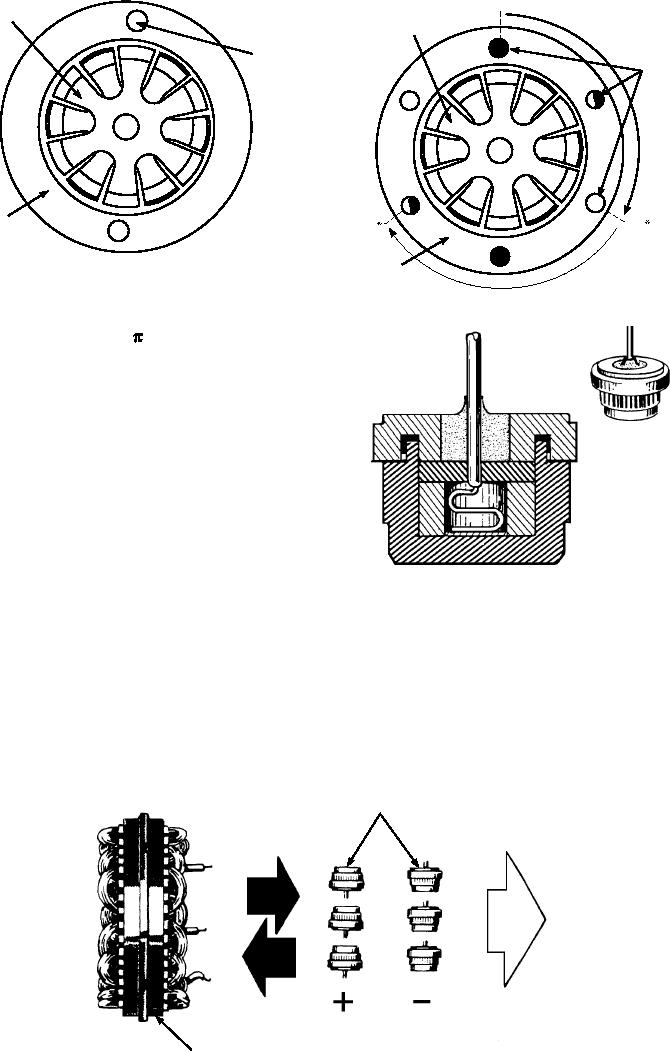
Figure 6-20.--A semiconductor (diode) rectifier.
rectifiers. The type of rectifier used in automotive
Identification of diode polarity varies greatly with
alternators is shown in figure 6-20--the semiconductor
the alternator model and manufacturer. Some are
diode. The silicon diode is the type most commonly
plainly marked with a + or sign, and some are marked
used. (Refer to NEETS, Module 7, for a more in-depth
with red and black lettering. Others are threaded to
explanation of diodes and rectifiers.)
indicate polarity--left for positive, right for negative.
Alternators have semiconductor rectifiers (diodes)
Automotive alternators use six diodes to provide
mounted within the alternator. The main advantages of
full-wave rectification of the alternator's three-phase
diodes over the previously used metallic rectifiers are
output, providing dc current at the output terminal. (See
that they have a higher current-carrying capacity, are of
fig. 6-21.) These six diodes (three positive and three
more rugged construction, and are small in size.
SIX DIODES
AC
DC
AC
ASf06021
STATOR
Figure 6-21.--Function of the alternator diode.
6-19

