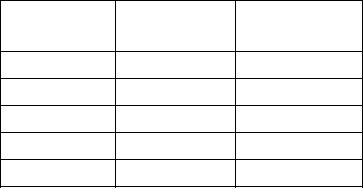
Table 11-2.--Boiling Points of Water
Convection is the transfer of heat by the movement
Feet Above Sea Pressure (psi)
Boiling Point of
of a medium (gas or liquid) through a space. Examples
Level
Water (F)
of this include a current of warm air through a room and
Sea level
14.70
212
warm air rising from a steam or hot water radiator.
2,000
13.57
208
Conduction
4,000
12.49
204
6,000
11.54
200
The transfer of heat from one molecule to another,
either of the same substance or of different substances,
8,000
10.62
196
by direct contact is called conduction. Physical contact
is necessary for conduction of heat, and the conduction
takes place from the region of higher temperature to the
It is not variations of pressure and temperature at
region of lower temperature. For example, if you take a
different altitudes that we are particularly interested in,
metal bar and place one end of it into a flame, the heat
but the relationship between the temperature of
passes from the flame to the bar, and then along the bar
vaporization (boiling point) and the corresponding
to your hand. Here, physical contact is made in each
pressure. And, it is not necessary to go to different
instance; flame to bar, bar to hand.
heights to obtain different pressures; different pres-
sures can be obtained by mechanical means at any
Suppose that you hold two metal bars in a flame,
location.
each of equal size, one bar of iron and the other of
copper. The heat conducted through the bar of copper
For example, a boiling liquid and its vapor may be
will reach your hand more quickly than through the bar
contained in an airtight metal cylinder with a piston. By
of iron because some substances conduct heat more
moving the piston in or out, the pressure within the
readily than others. This characteristic of a substance is
cylinder can be increased or decreased. If the piston is
called thermal conductance. The low or high thermal
pushed in, thus increasing the pressure inside, a
conductance of a material is of great importance in
thermometer will show that the change of state from
refrigeration and air conditioning. Some materials are
liquid to vapor requires a temperature higher than
used for heat transfer, while other materials are used to
212F. If the piston is pulled out, thus decreasing the
prevent heat transfer (insulators).
pressure within the cylinder, the thermometer shows
that the change of state from liquid to vapor takes place
PRESSURE-TEMPERATURE
at a temperature lower than 212F. This relationship of
RELATIONSHIPS
vaporization temperature and pressure, which varies for
different substances, follows an exact law, and may be
Pressure has a definite relationship to the boiling
tabulated accurately for almost any substance.
point of any liquid. As pressure is exerted on a liquid,
the temperature required to reach the boiling point of
APPLIED LAWS
the liquid also increases. Inversely, as you decrease the
pressure exerted on a liquid, the boiling point will also
As stated earlier, there are many laws that state how
decrease.
liquids and gases behave under different conditions.
Understanding these laws will help you understand the
If an uncovered container filled with fresh water at
operation of any type of equipment that uses
sea level is heated until the water boils, a thermometer
compression of liquids or gases. The three most
inserted in the water will show that its temperature is
important laws of compressed gases are Boyle's Law,
212F, and a barometer will show that the atmospheric
Charles' Law, and Dalton's Law.
pressure is about 14.7 psi. However, if the same pot of
water is placed on a hilltop 1,000 feet above sea level, at
Boyle's Law
boiling point the thermometer will read 210F, and the
barometer will show an atmospheric pressure of about
Boyle's law states: "The volume of a gas varies
14.14 psi. Similar variations in boiling point and
inversely to the pressure, provided the temperature
barometric pressure are observed at different altitudes,
remains constant."
as indicated in table 11-2.
11-4

