2-11.
2-12.
2-13.
2-14.
2-15.
2-16.
The most common emulsion is the
water-in-fuel emulsion.
What does
it look like?
1.
A light-to-heavy cloud
2.
A heavy-to-light cloud
3.
A dark, reddish haze
4.
A brown haze
A surfactant in fuel causes the
fuel and any water that contacts it
to mix easier, and also makes it
harder to separate.
1.
True
2.
False
Surfactants must be present for
microbiological growth to occur.
1.
True
2.
False
A surfactant problem can usually be
detected-by which of the following
observations ?
1.
2.
3.
4.
Dark, red-brown, or black water
in filter/separator sump
drains, refueler sump drains,
or pipeline low-point drains
Storage tanks not yielding a
clear, bright fuel after the
prescribed settling time
Triggering of fuel monitors in
delivery systems, if installed
All of the above
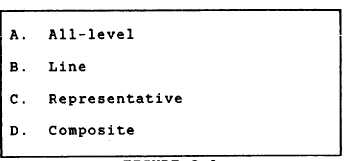
FIGURE 2-A
IN ANSWERING QUESTIONS 2-17 THROUGH 2-20,
SELECT FROM FIGURE 2-A THE TYPE OF FUEL
SAMPLE ASSOCIATED WITH EACH STATEMENT.
2-17.
Taken at or near the discharge
point of a hose immediately before
and during the first few minutes of
pumping.
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
2-18.
Consists of one container from a
large stock of package fuel of the
same grade and age.
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
2-19.
Contains a blend of individual
samples from several tanks that
contain the same type of product
being sampled.
What mechanical method. if any, is
used to separate commingled fuels?
1.
Settling
2.
Filtering
3.
Centrifuging
4.
None
Commingled fuels are usually caused
by
1.
leaking valves
2.
leaking tanks
3.
carelessness during handling
4.
intentional mixing
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
2-20.
Represents all fuel between the
drawoff level and the top surface
level of a tank.
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. D
9