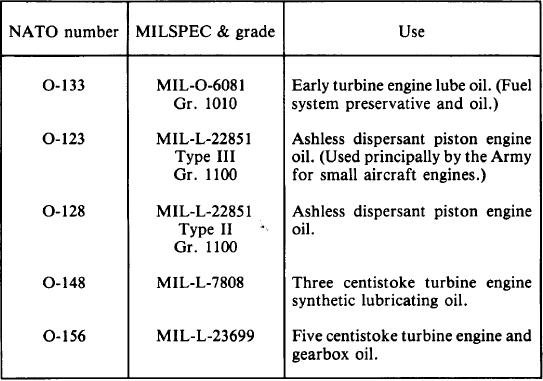
Table 5-1.-Classification of Lubricating Oils
especially where heat is concentrated; for example,
The contamination of oil by engine fuel can
in- the bearing compartments near hot turbine
result from a ruptured fuel-oil cooler. Since the
sections. This carbon eventually breaks off and
fuel system operates at a higher pressure than the
circulates through the engine lubricating system.
lube system, the flow will be into the oil supply.
The presence of fuel in the oil will cause oil
The pieces of carbon are usually not hard enough
or large enough to cause failure of the pumps.
dilution. It also changes the oil properties so the
However, they may be large enough to clog small
oil cannot cool and lubricate the bearings
properly.
filters or nozzles. The presence of sand, dirt, and
Another serious type of contamination is the
metallic particles in the lube system is another
oil itself. Synthetic oil will cloud or form other
source of operational contamination.
Faulty maintenance practices that contaminate
contaminants if stored too long. This is why there
is a shelf life for all synthetic oils. Never use
lubricating systems include using the wrong type,
overaged oil. Follow the applicable instruction for
or mixing oils, and improper servicing. The lube
shelf life of synthetic oil (it is usually 6 months)
system parts of an engine are made of materials
to prevent problems.
based upon the type of oil that is to be used.
Synthetic oils attack the common rubber materials
LUBRICATING GREASES AND
used in the O-ring, seals, and gaskets of lubrica-
THEIR PROPERTIES
tion systems that use mineral-based oil. This
attack causes the material to soften, swell, and
Another type of lubricant ADs should be
lose its ability to seal properly. This condition
familiar with is grease. Grease is used on bearings,
causes the oil to leak from the system.
outside the engine lubricating system, control
The contamination of oil by rust maybe due
arms and linkages, and actuators, The most
to water in the oil system. There is also contaminat-
important requirements of greases are as follows:
ion from storage containers or servicing equip-
1. Stability. It must be free from bleeding
ment. Over time, rust in the lube system will
(separation of oils), oxidation, and changes in
eventually discolor the bearings. Ordinary rust will
consistency during periods of storage and use.
leave a red discoloration on the bearing elements,
2. Noncorrosiveness. The lubricant must not
and black iron oxides will leave a black indica-
tion. These rust particles are not large enough to
chemically attack the various metals and other
material it comes in contact with.
cause pump failure.
5-3

