example, to cut down emission of light in a
2. The midget-flange type of light is for use
particular direction. Another bulb may be
in instrument panels and control boxes.
partially silvered to prevent emission in a specified
3. Fuselage and signal lights use lamps having
direction and/or to concentrate the light in other
two filaments in parallel to provide fast
directions. Some applications call for colored
signaling (smaller filaments heat and cool
bulbs; for example, in instrument illumination and
faster).
safety lights. The letters just before the military
specification (MS) dash number shows bulb
EXTERIOR LIGHTING
finish-R for red, SB for silvered bowl. If no
letter is present, the lamp is clear glass or frosted.
Many types of lights are used to meet the
You can also provide colored lighting by using
exterior lighting requirements of naval aircraft.
clear lamps with a colored lens cover.
The principal types of exterior lights are the
There are many special-purpose lamps in use
navigation or position lights, anticollision lights,
on naval aircraft. Three of the most common
landing lights, and formation lights.
types are listed below:
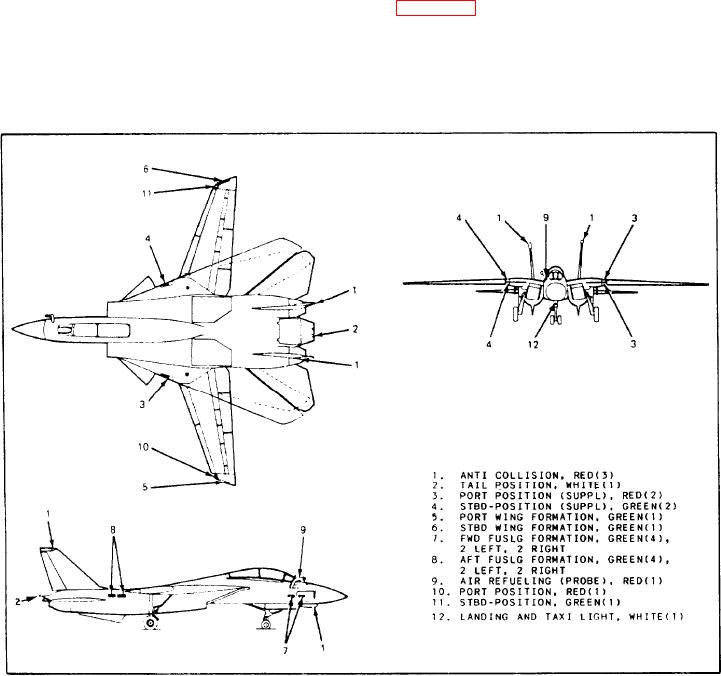
Figure 4-4 shows the components used in the
exterior lighting system of a carrier-type aircraft.
1. The parabolic, sealed-beam landing and
This figure shows the lights common to naval
taxi light. Signal lights also are used in
aircraft, but does not show every type of
sealed-beam lamps.
light in use on different aircraft. The lighting
Figure 4-4.-Exterior lighting.

