One of the floating contacts is in the door open
Q3. When does the fuel transfer center of
circuit and the other is in the door closed circuit.
gravity control system energize?
The two arms rest on a cam, which a small
motor constantly rotates. Thus, the floating
contacts are constantly vibrating toward the
central contact.
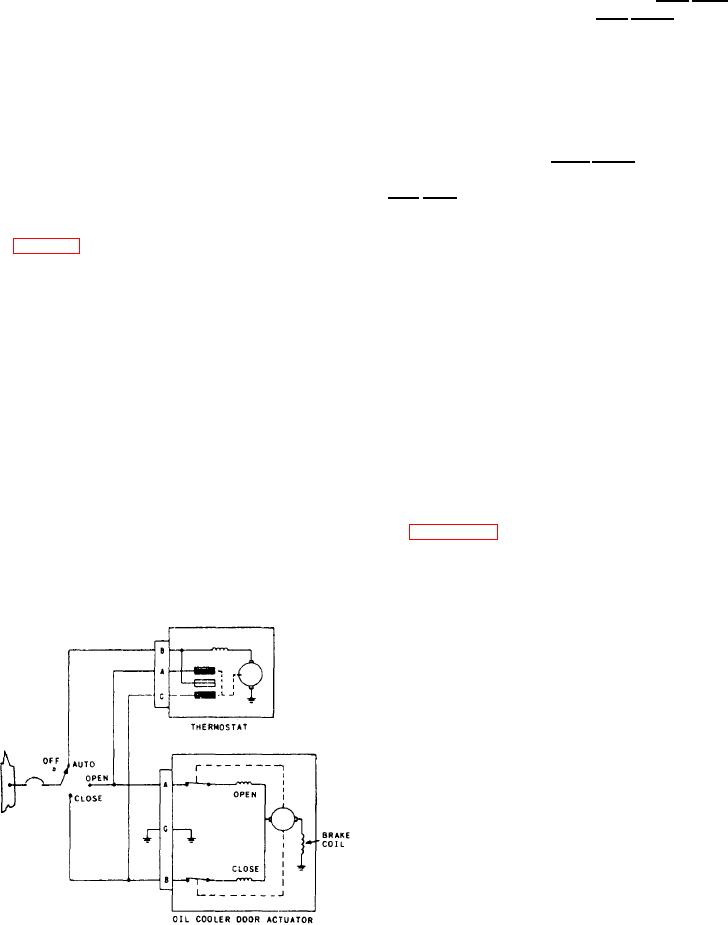
OIL TEMPERATURE CONTROL
When oil temperature rises above normal, the
SYSTEM
thermostatic element causes the central contact
Learning Objective: Recognize operating
to move toward the d o o r o p e n contact. As
principles and characteristics of aircraft
the contact vibrates, it intermittently closes the
door open circuit. As the actuator intermittently
engine oil temperature control systems.
energizes, the door slowly opens. When the oil
temperature returns to normal, the central contact
The cooling capacity of the oil cooler system
(fig. 5-15) in an aircraft depends on the airflow
moves back to a neutral position.
that passes through the cooler. Airflow is
When oil temperature falls below normal, the
controlled by an oil cooler door actuator, which
central contact moves in the opposite direction,
varies the oil cooler air exit duct.
closing the door. To prevent excessive hunting
The door actuator is a split-field, reversible
of the system, a tolerance is maintained by
an adjustment of the cam on the floating
dc motor. It includes a magnetic brake for
contact.
stopping it quickly when it reaches the limits of
travel. The control switch has four positions--
When the oil temperature rises high above the
OPEN, CLOSE, AUTOMATIC, and OFF. In the
normal value, the central contact lifts the floating
OPEN or CLOSE position, electrical power goes
contact clear of the cam, completing a continuous
to the actuator, which opens or closes the oil
circuit. The door then moves to the full open
cooler door. When the switch is in AUTO-
MATIC, a thermostat controls the actuator.
position where a limit switch in the actuator
breaks the circuit.
The thermostatic control unit is in the oil
return line. The unit contains two floating contact
Figure 5-16 shows another type of engine oil
arms and a central contact arm that actuates by
temperature regulator. This regulator has a
a bimetallic coil immersed in the oil return line.
mercury-filled thermostat, and relays auto-
matically control the position of the engine oil
cooler doors. When the engine temperature is low
requiring more heat, the two relays energize,
allowing the oil cooler door to close. As the
temperature increases, the thermostat completes
a path to ground, bypassing the relay coils and
de-energizing them. Power then goes through the
contact of one of the relays, opening the actuator
coil and causing the oil cooler door to open and
reduce engine temperature.
VARIABLE EXHAUST NOZZLE
CONTROL SYSTEM
Learning Objective: Recognize operating
conditions and features of aircraft engine
variable exhaust nozzle control systems.
As you read this section, refer to the simplified
schematic diagram of a typical variable exhaust
Figure 5-15.-Oil temperature control circuit.

