Figure 6-7.—Properly deburred tubing.
If neither tube cutter (standard or Permaswage) is
available, a fine-tooth hacksaw should be used to cut
tubing. A convenient method for cutting tubing with a
hacksaw is to place the tube in a flaring block and the
clamp block in a vise. After cutting the tube with a
hacksaw, remove all saw marks by filing the tube.
Tube Deburring
After you cut the tubing, remove all burrs and
sharp edges from inside and outside of tube (fig. 6-7)
with deburring tools. Clean out tubing. Make sure
that no foreign particles remain. A Permaswage
deburring tool may be used to remove burrs from
inside of tubing.
Select deburring tool and stem
subassembly (fig. 6-8) required for the size of tubing
to be deburred. Lubricate the sliding collar on the end
of elastic plug with light oil if necessary to get free
movement.
Engage threads and insert stem
subassembly into cutter end of deburring tool by
depressing the plunger, and screw stem subassembly
into plunger until it bottoms and fingertightens.
Check assembly deburring tool. Depress plunger and
the plug. Outside diameter should be reduced to the
same diameter as metal support collar on either end of
elastic plug. Release plunger. Two distinct circum-
ferential bumps will appear on elastic plug beyond
outside diameter of metal support collars. Check the
tube end for squareness. Check the elastic plug for
wear and cleanliness. Replace worn or damaged
elastic plug. Clean and lightly lubricate elastic plug
with lubricant compatible to hydraulic fluid to be used
Figure 6-8.—Permaswage deburring foot (typical).
in tubing. Grasp deburring tool in one hand with two
fingers on collar and thumb on plunger. Depress
plunger with thumb and insert elastic plug into tube
opening until cutter is about 1/8 inch from tube end.
If the plug fit is tight due to a large burr on ID of the
tube, slowly rotate the plunger end of tool while
gently pushing tool into the tube end. Release
plunger to allow elastic plug to expand and seal tube
opening to prevent chips from entering. Hold tube
end and rotate knurled body of deburring tool in a
clockwise direction while applying pressure to cutter.
Continue rotating tool until resistance decreases,
indicating all burrs have been removed from tube ID.
You should avoid excessive deburring, which can
cause too deep a chamfer on tube ID. The chamfer
should not exceed one-half wall thickness of tubing.
Relax pressure and rotate deburring tool several times
to produce a smooth surface. Without depressing
plunger, ease deburring tool from tube until the first
bulge of elastic plug is exposed. Wipe off the tube
end and plug.
Check the tube end to see if it is
completely deburred. If tube end appears saticfactory,
without depressing plunger, remove deburring tool
from tube. If tube end is not completely deburred,
without depressing plunger, push deburring tool back
into the tube and repeat all the steps.
TUBE BENDING
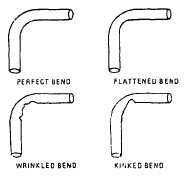
The objective in tube bending is to obtain a
smooth bend without flattening the tube. Acceptable
and unacceptable bends are shown in figure 6-9.
Tube bending is usually done by using a mechanical
or hand-operated tube bender. In an emergency, soft,
nonheat-treated aluminum tubing smaller than
1/4 inch in diameter may be bent by hand to form the
desired radius.
Figure 6-9.—Tubing bends.
6-9