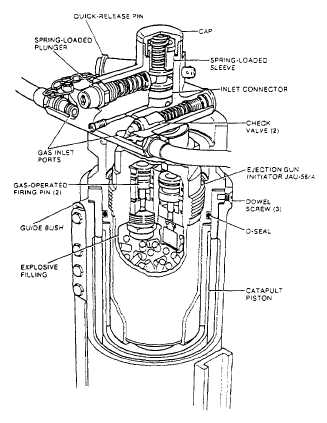
Figure 5-4.-Ejection gun initiator (JAU-56/A) and catapult
manifold valve.
and provides the initial power for the ejection of
the seat. The catapult consists of an outer barrel
and an inner telescopic piston. The barrel is
attached to the aircraft structure, and the piston
and barrel are engaged at the top end by the top
latch plunger installed in the main beams
assembly.
The catapult assembly is operated by explosive
charges. Assembly operation is discussed later in
this chapter.
BARREL.— The barrel is a built-up structure
consisting of a light alloy tube to which are
permanently attached top and bottom end fittings.
A housing situated towards the bottom end
contains the secondary cartridge. Five brackets
support two guide rails bolted on the outboard
sides of the tube. The bottom end fitting
incorporates the lower mounting bracket for
attaching the catapult to the aircraft and studs for
attachment of the ballistic latches.
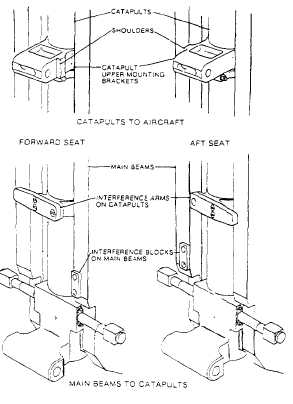
The upper mounting consists of a bracket
clamped on the barrel towards the upper end. It
incorporates an interference shoulder on one side
to ensure location of the catapult in the correct
cockpit (fig. 5-5). An interference arm mounted
on one of the guide rail brackets ensures that the
correct main beams assembly is installed. A
crossbeam secured to the barrel provides an
anchorage point for the RH ballistic manifold
quick-disconnect lanyard. The top end fitting of
the barrel has a square aperture, the barrel latch,
through which the plunger of the top latch
mechanism fitted on the seat main beam protrudes
when the seat is installed on the catapult. A guide
bushing, fitted in the internal diameter of the top
end fitting, is secured by three dowel screws; at
the end of the catapult stroke, the dowel screws
are sheared by the head of the piston striking the
guide bushing. The piston then separates from the
barrel, and the guide bushing remains on the
piston (fig. 5-3).
BALLISTIC LATCHES.— Two ballistic
latches are attached to the bottom end fitting by
studs and nuts. Each latch comprises a body,
which is internally drilled to form a cylinder and
contains a spring-loaded piston. When operated
during the ejection sequence, gas pressure from
within the catapult acts on the latch pistons,
Figure 5-5.-Interference devices, forward and aft seats.
5-6