twin-barrel electromechanical actuator (fig. 6-4),
which is driven by a 115/200-volt, 400-Hz, three-
phase, four-pole induction motor. The motor is
geared to a reduction gear train, which drives two
screw barrels that are attached to mating flanges
on the base of the rocket catapult. The rocket
catapult is bolted to the top of the seat structure,
which allows a 5.5-inch up and down adjustment
of the seat parallel to the guide rails. Six rollers
on the seat allow the seat to move up or down
the guide rails.
ROCKET CATAPULT.— The rocket catapult
provides the necessary propulsion to eject the seat
and crew member from the aircraft during the
ejection sequence. The performance capability of
the rocket catapult at zero altitude and zero
airspeed reduces the effects of high sink rate and
nosedown attitudes encountered during critical
approach and landing operations. The rocket
catapult is secured at the top center of the seat
back, and is supported at the base by twin
barrels of the seat adjustment actuator. Two
attachments on the actuator secure the actuator
to the aircraft bulkhead.
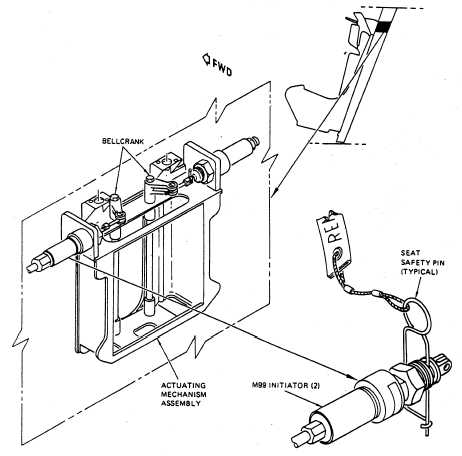
M99 INITIATORS.— Two M99 initiators
are installed on the M99 initiator actuating
mechanism (fig. 6-5) near the top of each canted
bulkhead behind the pilot’s and copilot’s seats,
and one M99 initiator is installed at each tactical
air coordinator (TACCO) and sensor operator
(SENSO) seat location. The M99 initiator is a
mechanically fired, pressure-developing source.
Each M99 initiator, consisting of a constant-
volume cylinder with a tube connection at one
end, contains a mechanically fired mechanism and
cartridge. The M99 initiator firing mechanism can
be secured in a safe position by a safety pin that
passes through the cap and a groove on the side
of the M99 initiator pin. Pulling either the primary
or secondary ejection control handle initiates the
ejection sequence, which, in turn, rotates the
firing control disconnect, moves two firing rods
Figure 6-5.—M99 initiator location.
6-9