means that the spindle has moved away from the
anvil an additional 10 times 0.001 inch, or 0.010
inch. Add this amount to the 0.250 inch sleeve
reading, and the total distance is 0.260 inch.
Reading a Vernier Micrometer Caliper
Many times you are required to work to
exceptionally precise dimensions. Under these
conditions you should use a micrometer that is
accurate to ten thousandths of an inch. This
degree of accuracy is obtained by the addition of
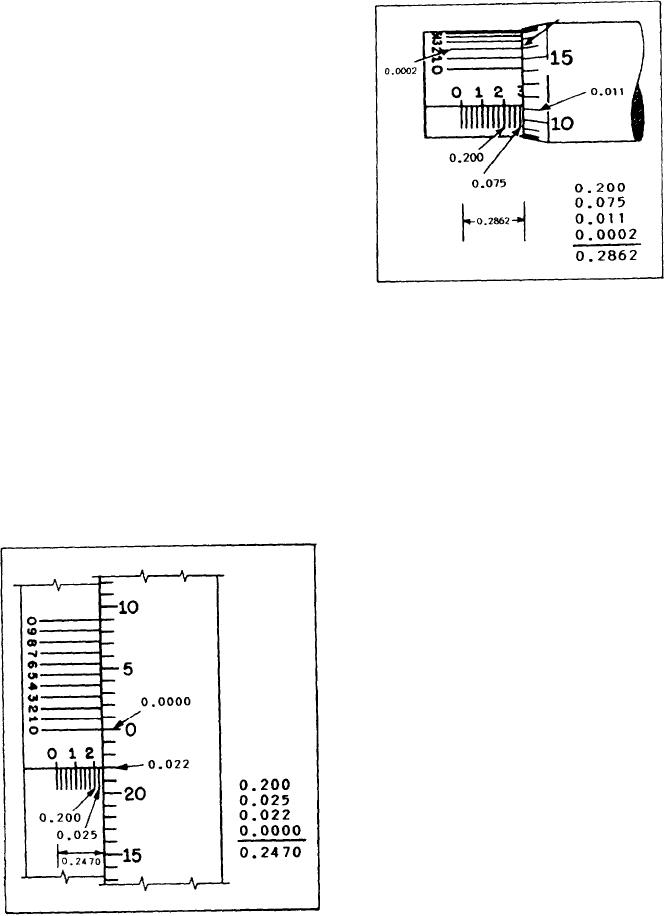
a vernier scale. This scale (fig. 3-23) furnishes the
fine readings between the lines on the thimble
rather than making you estimate. The 10 spaces
on the vernier are equivalent to 9 spaces on the
thimble. Therefore, each unit on the vernier scale
is equal to 0.0009 inch, and the difference
between the sizes of the units on each scale is
Figure 3-24.--Read a vernier micrometer caliper.
0.0001 inch.
When a line on the thimble scale does not
an inch beyond the horizontal sleeve line. When
coincide with the horizontal sleeve line, you can
you add this to the other readings, the reading will
determine the additional space beyond the
be 0.200 + 0.075 + 0.011 + 0.0002 = 0.2862
readable thimble mark by finding which vernier
of an inch, as shown.
mark coincides with a line on the thimble scale.
Add this number, as that many ten thousandths
of an inch, to the original reading. In figure 3-24,
TEST EQUIPMENT
see how the second line on the vernier scale
As a GSE or a GSM, you are responsible for
coincides with a line on the thimble scale.
operating various pieces of test equipment when
This means that the 0.011 mark on the thimble
performing maintenance and repair procedures.
scale has been advanced an additional 0.0002 of
You must fully understand the operation of this
test equipment and must be able to interpret the
results of these tests.
Some of the equipment you will find in use are
gauge calibration equipment, vibration analysis
equipment, horoscopes, fuel testing equipment,
and electrical/electronic test equipment.
DEADWEIGHT TESTER/GAUGE
COMPARATOR
Several types of deadweight testers are
available. The types are determined by whether
the pressure medium is fluid or gas. The fluid
deadweight testers use oil or water as the pressure
medium; bifluid deadweight testers use oil and
water. Pneumatic deadweight testers use a gas,
usually pure nitrogen, as the pressure medium.
You will ONLY use the deadweight tester/
gauge comparator to compare a gauge to a known
pressure. You will do this by applying a pressure
with the pump to the standard comparator gauge
and the gauge to be compared.
Since the construction details vary for the
different types of testers, you should read the
manufacturer's catalog or the applicable Naval
Figure 3-23.--Vernier scale on a micrometer.
3-16

