ECSS to indicate the status of the shifting lever.
Override stops are provided on the clutch and
shaft lock limit switch brackets to prevent the
shifting levers from moving past the microswitch
positions.
The turning gear shifting lever is connected to
the turning gear clutch via the clutch shaft.
Shifting this lever can engage or disengage
the clutch from the shaft adapter. The shifting
levers can be padlocked to the disengaged
positions to prevent accidental engagement of
the turning gear while the MRG is operating.
Two plates on the clutch limit switch bracket iden-
tify the shifting lever position: TURNING GEAR
D I S E N G A G E D and TURNING GEAR
ENGAGED. The connect-disconnect coupling
moves in the axial direction to engage or
disengage. The shifting lever axially engages or
disengages the internal gear teeth with mating
teeth on the end of the second-reduction pinion
shaft.
The turning gear provides a means for rotating
the propeller shaft while the propulsion plant is
shut down. The second-reduction gear shaft and
propeller shaft rotate at about 0.1 rpm with the
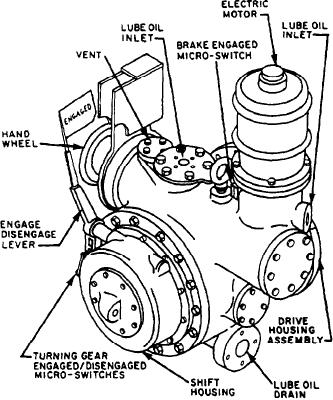
Figure 8-11.--Turning gear assembly (FFG class ships).
turning gear engaged and operating. This slow
speed permits inspection of the MRG gear teeth.
When the turning gear is locked, a microswitch
The slow rpm also permits MRG cooldown
that is actuated by the brake lever provides a brake
without shaft distortion or bending. Turning also
locked signal to the PCC. A handwheel is also
prevents propeller shaft bowing. The circuit
provided for turning the turning gear manually.
permissives which must be satisfied to engage
The gearbox for the turning gear has a worm gear
the turning gear are as follows:
drive system.
Shaft not locked
The electric motor is controlled by a magnetic
controller that is mounted remotely from the
Greater than 9 psig lube oil pressure
MRG. The motor is designed to operate in either
No GTE running
the forward or reverse direction.
No clutch engaged (Turning gear motor can-
Lubricating Pump
not be engaged if either clutch is engaged.)
The lube oil system in each MER incorporates
three positive-displacement pumps. Two of the
FFG CLASS SHIPS.--Figure 8-11 shows the
pumps are driven by electric motors, while the
turning gear assembly on the FFG class ships. It
third is driven by the MRG and is designated the
is mounted on the aft end of the port HS pinion.
attached pump. The purpose of the attached
It has a shift lever for engagement or disengage-
pump is to augment the output of the electric
ment. Two microswitches associated with the shift
pumps during propulsion plant operation. This
lever provide electrical signals to the propulsion
pump is a vertical-screw, submerged-suction
control console (PCC) and the local operating
pump, with a nominal flow of 1,140 gpm at 1,220
panel (LOP) when the shift lever is engaged or
rpm pump speed. The motor-driven pumps are
disengaged.
of similar construction, but they have a smaller
The turning gear assembly includes a 5-hp
capacity.
electric motor that operates from a 440-volt,
The attached pump is driven by the lower
60-hertz, 3-phase power source, The coupling
inboard second-reduction pinion shaft through a
between the electric motor and the turning gear
manually operated connect/disconnect coupling
train includes a mechanically operated brake. This
and a right-angle drive unit. Figure 8-12 shows
brake is used to lock the turning gear and may
this right-angle drive.
also be used to lock the entire reduction gear train.
8-20

