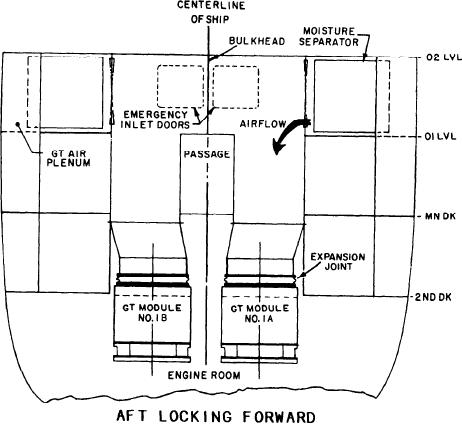
Figure 2-14.--FFG air intake system.
duct. The permanently installed rails extend
Besides the ducting, the GTE uptake and
through the high hat section. These serve to guide
intake system includes moisture separator
the engine as it is lifted vertically from the ship.
assemblies, emergency inlet doors, and cooling air
Removal of the engine is accomplished in two
fans (not shown). Also included are cooling air
operations due to space constraints. The GG is
bypass dampers and provisions for anti-icing
separated from the PT while still in the enclosure.
upstream and downstream of the moisture
Then it is removed from the ship, followed by
separators (not shown).
removal of the PT.
Demister Panels
The demister panels (or moisture separators)
FFG INLET DUCT SYSTEM
are of knit wire mesh construction mounted in a
Refer to figure 2-14 as we discuss the FFG
supporting frame. They remove moisture droplets
inlet duct system. The GTE uptake spaces and
containing sea salt and prevent other foreign
objects from entering the intake and cooling air
intake system house three separate ducting systems
per GTE. They are for combustion air, module
ducts. In operation, the moisture droplets adhere
cooling air, and exhaust gas elimination.
to the wire mesh while the air passes through. The
Atmospheric air for the combustion and cooling
moisture droplets coalesce into larger drops and
air ducting normally enters through the intake
fall free of the airstream. They then drain into
plenums. These are located on each side of the
troughs which are piped to the plumbing drains
ship's structure. The air is then carried through
system. Each combustion air intake duct has eight
ducting to the GTMs in the engine room below.
demister panels. Each cooling air intake duct has
Ducting connections to the GTMs are made via
four panels.
expansion joints on top of each GTM. The
Blow-In Doors
combustion air intake ducts also provide the
access for removal and replacement of the engine
Emergency inlet (blow-in) doors are provided
GG and PT sections.
in the combustion air and cooling air ducts to each
2-13

