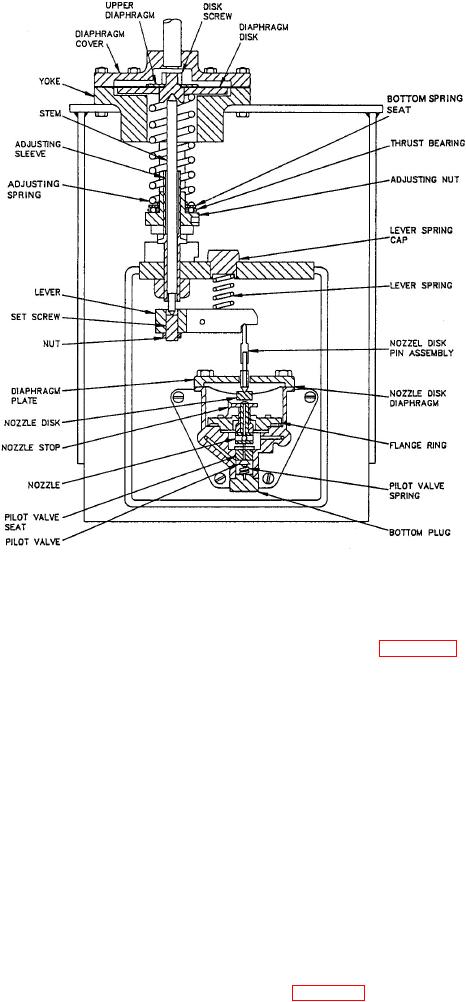
Figure 4-4.-External control pilot.
hole and stem collar seal for air leakage, and check
external air source with an in-line pressure regulator
the externally mounted pilot controllers, such as the
that is connected to the diaphragm inlet air
one shown in figure 4-4, for proper supply air
connection. With the air pressure regulator set at
pressure settings.
zero psi, the valve position indicator should be
pointing at zero percent on the position scale,
TEMPERATURE CONTROL VALVES. The
indicating a normally closed valve. As you apply air
pressure to the diaphragm, the valve should begin to
types of temperature control valves we normally use
open. The amount of air pressure you apply to the
are either the air pilot operated valves, such as the
valve will determine the percent of valve opening,
one we described earlier, or the spring-loaded,
depending on the valve spring pressure. Normally, all
bellows-actuated valves. These two valves are used in
of these valves will require approximately 5 psi of air
almost every system in the engineering plant. You
pressure to start valve stem movement. At 20 to 22
will find either one located near every heat exchanger
psi, the valve should be fully open. If more air
in the plant.
pressure than 22 psi is required to move the valve
stem, there is a good possibility the diaphragm has a
Pilot Operated Valves. The tests and
hole in it, the stem seal is leaking, or the valve is
inspections you will use for the pilot operated valves
binding. Any one of these problems can seriously
are the same as those we previously described for the
affect the responsiveness of the valve, so you should
level control valves.
investigate these conditions as soon as possible.
Spring-Loaded Bellows Actuated Valves. A
Generally, you will perform an inspection of a pilot
typical spring-loaded bellows actuated valve is shown
operated valve during normal valve operation.
in figure 4-5. For this valve, you will normally
During the inspection, you will need to check the
conduct
packing gland for leakage, watch the stem cycle for
smooth operation, examine the diaphragm telltale

