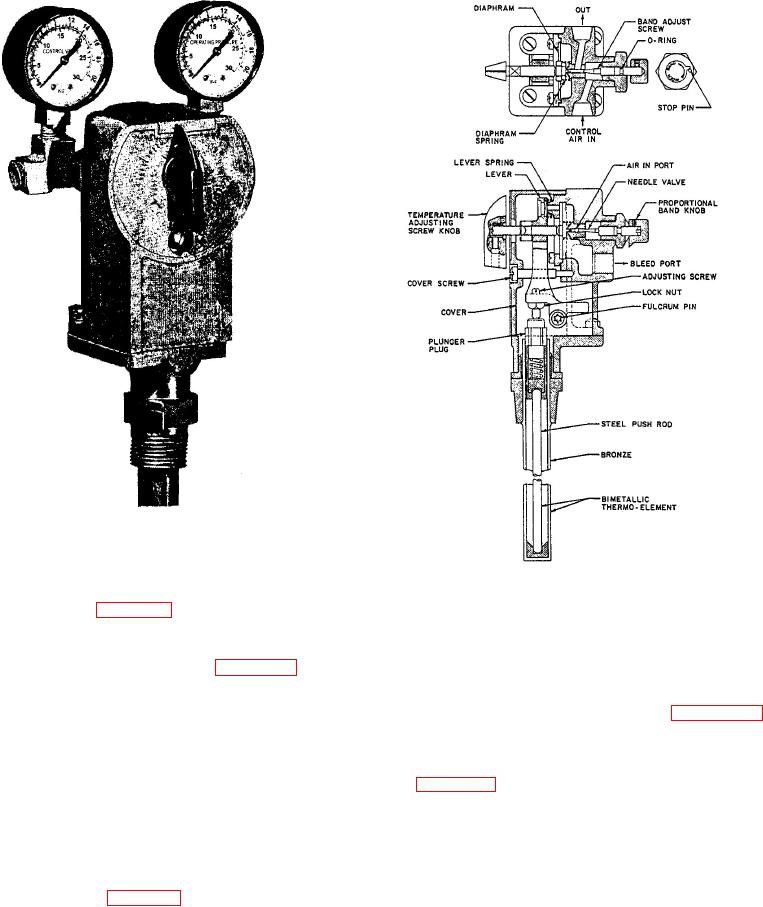
Figure 4-1.-Bimetallic temperature pilot
controller.
The externally mounted temperature pilot
Figure 4-2.-Detail drawing of a bimetallic
controller shown in figure 4-1 is used in most gas
temperature pilot controller.
turbine MRG LO systems. It receives inputs from the
increasing or decreasing length of the bimetallic
NOTE
sensing element, as shown in detail in figure 4-2, The
sensing bulb is installed in the MRG LO cooler outlet
Remember, our description of this operation
piping where it senses the oil temperature before the
pertains only to the controller shown in figure 4-2.
oil enters the MRG. The tube, which is fixed at one
Normally, most automatic temperature control
end, expands and contracts with temperature
valves used for cooling will fail to the open
changes. Since there is a difference in the coefficient
position. Our description and the controller shown
of expansion between the tube and the Invar rod,
in figure 4-2 are intended to provide you with a
temperature changes at the tube will create
basic example of controller operation.
movement of the rod. The movement of the rod is
transmitted and amplified by a lever that contacts the
VALVE ACTUATORS. As well as automatic
diaphragm assembly. As the rod moves, it regulates
control valves, there are several types of valve
the amount of air pressure that is sent to or bled off
actuators. Many actuators are pneumatic, such as the
the automatic control valve. For example, if the
one in the automatic temperature control valve we
controller shown in figure 4-2 should sense an
just described. Some valve actuators are mechanical.
increase in liquid temperature, it will cause the tube
A large number of valve actuators you will encounter
to lengthen, allowing a downward movement of the
are electrical (solenoid type).
rod, which, in turn, will increase airflow to the
automatic control valve. Consequently, a temperature
The mechanical actuators, either spring-loaded or
increase will cause the automatic control valve to
manual, are stand alone operators or are sometimes
open, thereby increasing the cooling medium or the
used
oil flow (depending on system design) through the
cooler.

