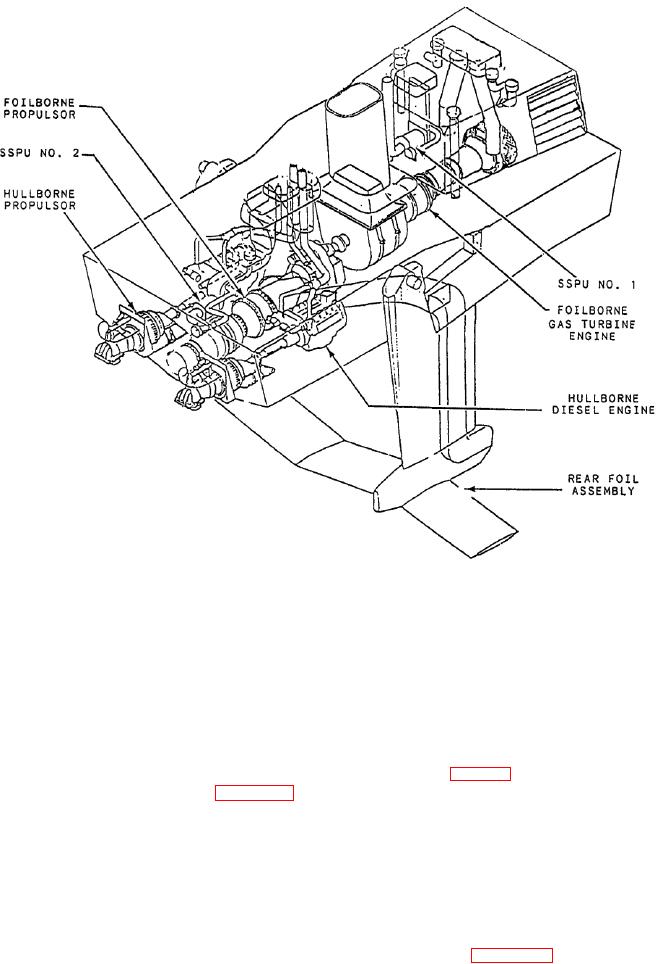
Figure 6-20.--Main machinery arrangement for foilborne and hullborne propulsion systems.
foilborne operations. By providing trim and attitude
hullborne system. As its name implies, the foilborne
control, automatic banking in turns, and seaway
propulsion system propels the ship in the foilborne
disturbance alleviation, the foilborne control system
mock In addition, the foilborne system can propel the
makes it possible for the PHM to achieve its desirable
ship in the hullborne mode, either with the foils
riding qualities and fast speeds. The foilborne control
extended or retracted. The hullborne propulsion
surfaces include the trailing edge flaps on each of the
system, however, can propel the ship only in the
foils and the swiveled forward strut which acts as a
hullborne mode, either with the foils up or down. The
rudder. (See fig. 6-20.) In the following paragraphs,
machinery arrangement for both the foilborne and
we will get a closer look at both the hullborne and
hullborne propulsion systems is shown in figure 6-20.
foilborne propulsion systems. Let's first look at the
foilborne system.
Both foilborne and hullborne operations are
controlled from a common helm. When the PHM is in
the hullborne mode, a water jet nozzle pivots in
FOILBORNE PROPULSION SYSTEM
response to an operator command from the helm to
provide steering and reversing functions. A bow
The foil borne propulsion system provides
thruster provides for close-in maneuvering and
the PHM with speed and stability. The basic
docking. Consequently, the hullborne mode is used
components of the foilborne propulsion system
for any type of close maneuvering, such as docking or
are shown in figure 6-21. The foilborne power
reversing the craft's direction. When the craft is in
plant supplies the thrust required for takeoff
the foilborne mode, a control system consisting of the
and foilborne operations. Foilborne propulsion is
helm, throttle, and an automatic control system
created by a 2-stage water jet pump powered by
(ACS) provides continuous dynamic control during all
a gas turbine engine. The propulsion thrust

